- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
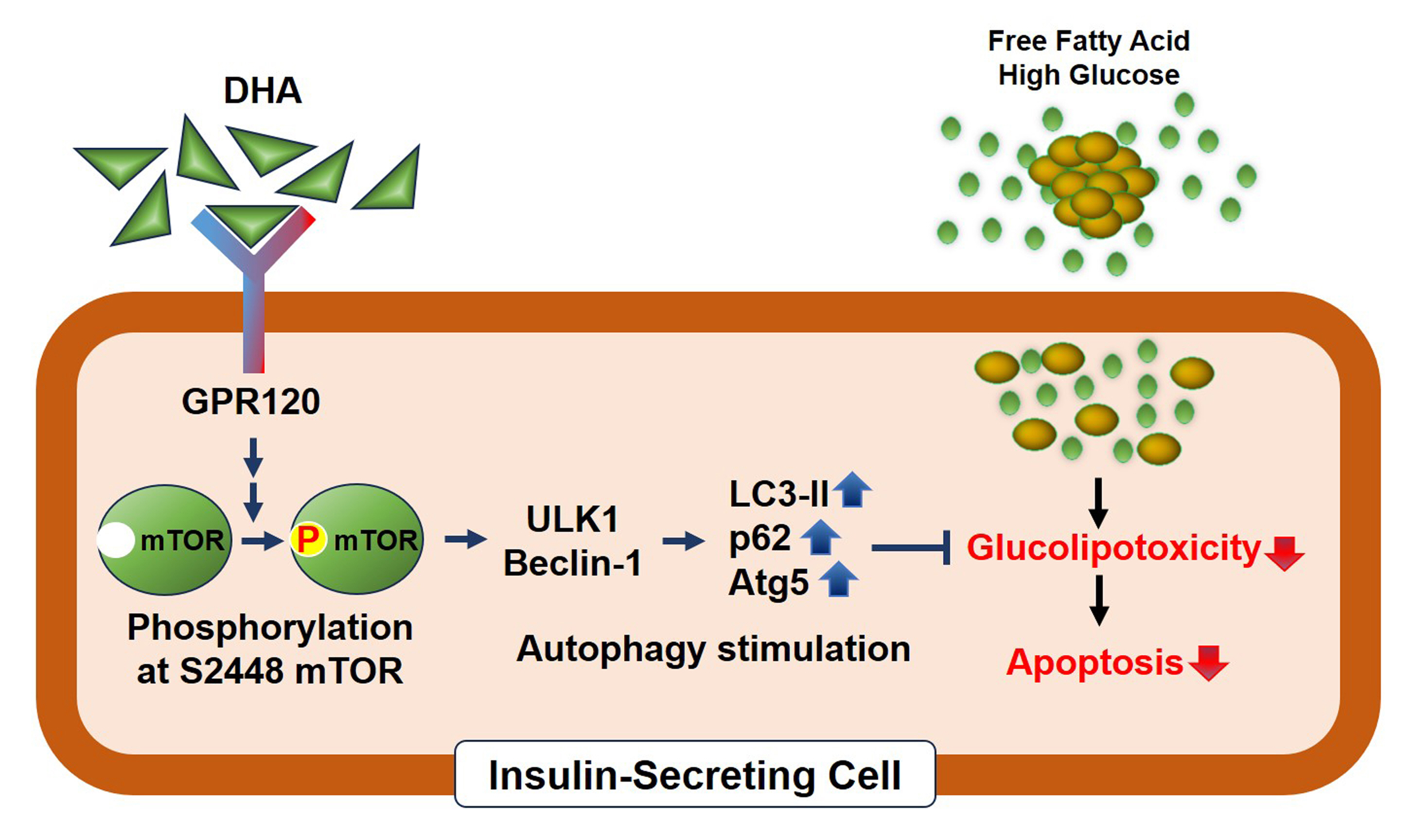
- Docosahexanoic Acid Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Apoptosis by Autophagy Upregulation via GPR120/mTOR Axis in Insulin-Secreting Cells
-
Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):353-363. Published online January 23, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1809
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) reportedly have protective effects on pancreatic β-cells; however, the underlying mechanisms are unknown.
Methods
To investigate the cellular mechanism of PUFA-induced cell protection, mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells were cultured with palmitic acid (PA) and/or docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alterations in cellular signaling and apoptosis were examined.
Results
DHA treatment remarkably repressed caspase-3 cleavage and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive red dot signals in PA-treated MIN6 cells, with upregulation of autophagy, an increase in microtubule- associated protein 1-light chain 3 (LC3)-II, autophagy-related 5 (Atg5), and decreased p62. Upstream factors involved in autophagy regulation (Beclin-1, unc51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 [ULK1], phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin [mTOR], and protein kinase B) were also altered by DHA treatment. DHA specifically induced phosphorylation on S2448 in mTOR; however, phosphorylation on S2481 decreased. The role of G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) in the effect of DHA was demonstrated using a GPR120 agonist and antagonist. Additional treatment with AH7614, a GPR120 antagonist, significantly attenuated DHA-induced autophagy and protection. Taken together, DHA-induced autophagy activation with protection against PA-induced apoptosis mediated by the GPR120/mTOR axis.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that DHA has therapeutic effects on PA-induced pancreatic β-cells, and that the cellular mechanism of β-cell protection by DHA may be a new research target with potential pharmacotherapeutic implications in β-cell protection.
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
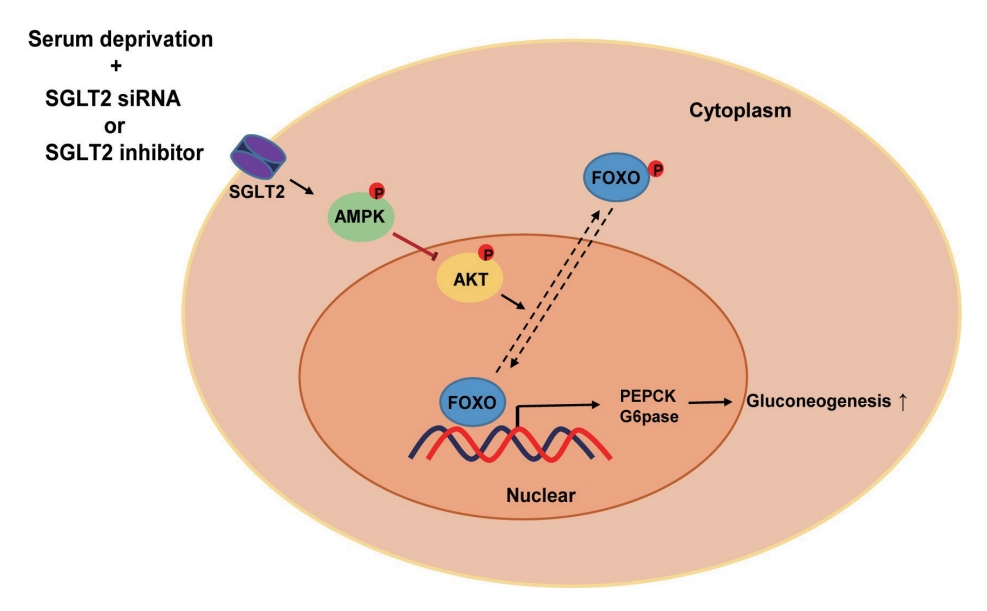
- Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 during Serum Deprivation Increases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO Signaling Pathway
-
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Yu-Mi Lim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):98-108. Published online January 3, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1786
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) mediates glucose reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules, and SGLT2 inhibitors are used as therapeutic agents for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study aimed to elucidate the effects and mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibition on hepatic glucose metabolism in both serum deprivation and serum supplementation states.
Methods
Huh7 cells were treated with the SGLT2 inhibitors empagliflozin and dapagliflozin to examine the effect of SGLT2 on hepatic glucose uptake. To examine the modulation of glucose metabolism by SGLT2 inhibition under serum deprivation and serum supplementation conditions, HepG2 cells were transfected with SGLT2 small interfering RNA (siRNA), cultured in serum-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium for 16 hours, and then cultured in media supplemented with or without 10% fetal bovine serum for 8 hours.
Results
SGLT2 inhibitors dose-dependently decreased hepatic glucose uptake. Serum deprivation increased the expression levels of the gluconeogenesis genes peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1 alpha (PGC-1α), glucose 6-phosphatase (G6pase), and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), and their expression levels during serum deprivation were further increased in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA. SGLT2 inhibition by siRNA during serum deprivation induces nuclear localization of the transcription factor forkhead box class O 1 (FOXO1), decreases nuclear phosphorylated-AKT (p-AKT), and p-FOXO1 protein expression, and increases phosphorylated-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK) protein expression. However, treatment with the AMPK inhibitor, compound C, reversed the reduction in the protein expression levels of nuclear p- AKT and p-FOXO1 and decreased the protein expression levels of p-AMPK and PEPCK in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA during serum deprivation.
Conclusion
These data show that SGLT2 mediates glucose uptake in hepatocytes and that SGLT2 inhibition during serum deprivation increases gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway.
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
-
Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):568-577. Published online October 10, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1770
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) has become an important tool for evaluating cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study evaluated the significance of CACS for future CVD through more than 10 years of follow-up in asymptomatic Korean populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) known to have a relatively low CACS burden.
Methods
We enrolled 981 asymptomatic T2DM patients without CVD at baseline who underwent CACS evaluation using multidetector computed tomography between January 2008 and December 2014. They were grouped into five predefined CACS categories based on Agatston scores and followed up by August 2020. The primary endpoint was incident CVD events, including coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial disease.
Results
The relative risk of CVD was significantly higher in patients with CACS ≥10, and the significance persisted after adjustment for known confounders. A higher CACS category indicated a higher incidence of future CVD: hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) 4.09 (1.79 to 9.36), 12.00 (5.61 to 25.69), and 38.79 (16.43 to 91.59) for 10≤ CACS <100, 100≤ CACS <400, and CACS ≥400, respectively. During the 12-year follow-up period, the difference in event-free survival more than doubled as the category increased. Patients with CACS below 10 had very low CVD incidence throughout the follow-up. The receiver operating characteristic analysis showed better area under curve when the CACS cutoff was 10 than 100.
Conclusion
CACS can be a sensitive marker of CVD risk. Specifically, CACS above 10 is an indicator of CVD high-risk requiring more intensive medical treatment in Koreans with T2DM.
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
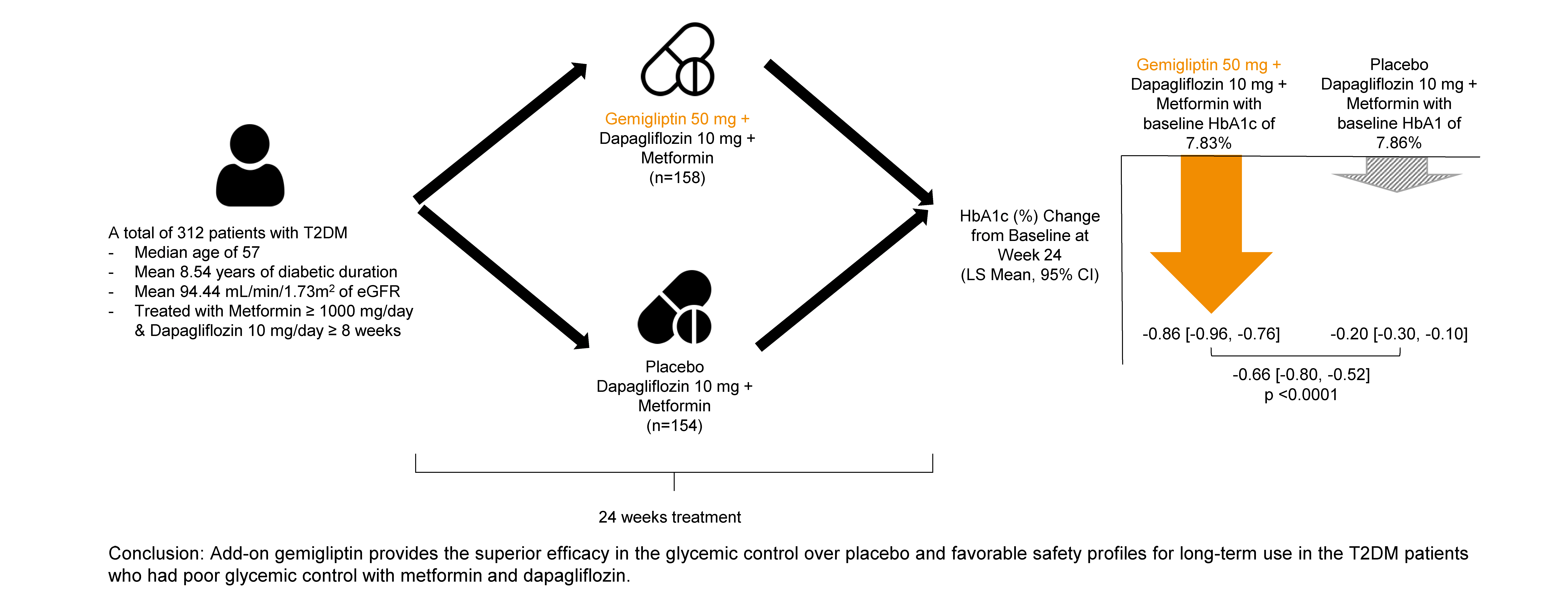
- Efficacy of Gemigliptin Add-on to Dapagliflozin and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study (SOLUTION)
-
Byung Wan Lee, KyungWan Min, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Bon Jeong Ku, Jun Goo Kang, Suk Chon, Won-Young Lee, Mi Kyoung Park, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Keeho Song, Soon Jib Yoo
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):328-337. Published online June 28, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1688
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of add-on gemigliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who had inadequate glycemic control with metformin and dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, double-blind, phase III study, 315 patients were randomized to receive either gemigliptin 50 mg (n=159) or placebo (n=156) with metformin and dapagliflozin for 24 weeks. After the 24-week treatment, patients who received the placebo were switched to gemigliptin, and all patients were treated with gemigliptin for an additional 28 weeks.
Results
The baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups, except for body mass index. At week 24, the least squares mean difference (standard error) in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) changes was –0.66% (0.07) with a 95% confidence interval of –0.80% to –0.52%, demonstrating superior HbA1c reduction in the gemigliptin group. After week 24, the HbA1c level significantly decreased in the placebo group as gemigliptin was administered, whereas the efficacy of HbA1c reduction was maintained up to week 52 in the gemigliptin group. The safety profiles were similar: the incidence rates of treatment-emergent adverse events up to week 24 were 27.67% and 29.22% in the gemigliptin and placebo groups, respectively. The safety profiles after week 24 were similar to those up to week 24 in both groups, and no new safety findings, including hypoglycemia, were noted.
Conclusion
Add-on gemigliptin was well tolerated, providing comparable safety profiles and superior efficacy in glycemic control over placebo for long-term use in patients with T2DM who had poor glycemic control with metformin and dapagliflozin.
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
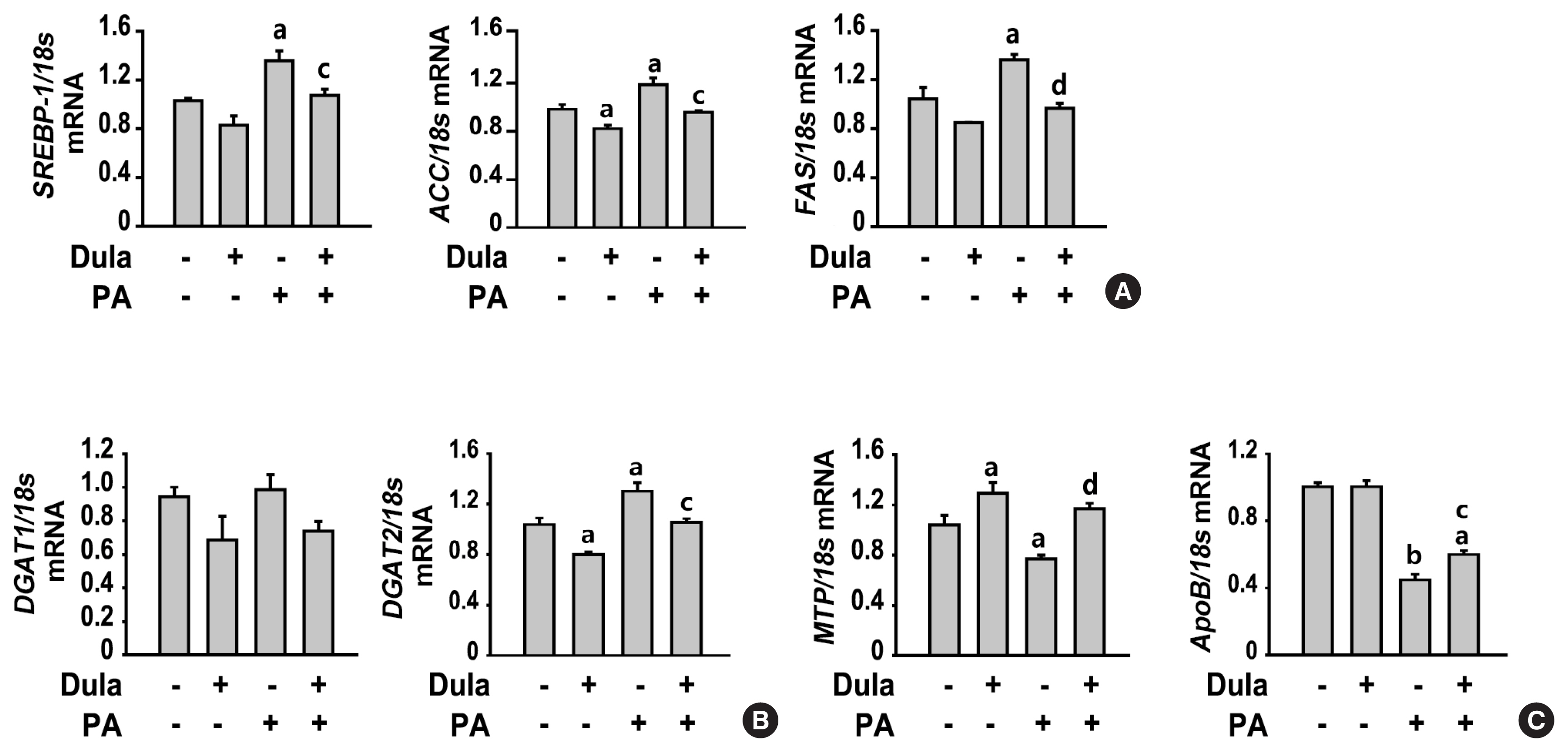
- Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
-
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):74-83. Published online February 9, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1293
-
-
4,882
View
-
235
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Dulaglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), has been shown to reduce body weight and liver fat content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Family with sequence similarity 3 member A (FAM3A) plays a vital role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. The aim of this study was to determine the mechanisms by which dulaglutide protects against hepatic steatosis in HepG2 cells treated with palmitic acid (PA).
Methods
HepG2 cells were pretreated with 400 μM PA for 24 hours, followed by treatment with or without 100 nM dulaglutide for 24 hours. Hepatic lipid accumulation was determined using Oil red O staining and triglyceride (TG) assay, and the expression of lipid metabolism-associated factor was analyzed using quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting.
Results
Dulaglutide significantly decreased hepatic lipid accumulation and reduced the expression of genes associated with lipid droplet binding proteins, de novo lipogenesis, and TG synthesis in PA-treated HepG2 cells. Dulaglutide also increased the expression of proteins associated with lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation and FAM3A in PA-treated cells. However, exendin-(9-39), a GLP-1R antagonist, reversed the expression of FAM3A, and fatty acid oxidation-associated factors increased due to dulaglutide. In addition, inhibition of FAM3A by siRNA attenuated the reducing effect of dulaglutide on TG content and its increasing effect on regulation of fatty acid oxidation.
Conclusion
These results suggest that dulaglutide could be used therapeutically for improving nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and its effect could be mediated in part via upregulation of FAM3A expression through a GLP-1R-dependent pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - GLP-1/GLP-1RAs: New Options for the Drug Treatment of NAFLD
Haoran Jiang, Linquan Zang
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(2): 100. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Riccardo Nevola, Raffaella Epifani, Simona Imbriani, Giovanni Tortorella, Concetta Aprea, Raffaele Galiero, Luca Rinaldi, Raffaele Marfella, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1703. CrossRef - FAM3A mediates the phenotypic switch of human aortic smooth muscle cells stimulated with oxidised low-density lipoprotein by influencing the PI3K-AKT pathway
Lei Yang, Baoshun Du, Shitao Zhang, Maode Wang
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal.2023; 59(6): 431. CrossRef - ATP Secretion and Metabolism in Regulating Pancreatic Beta Cell Functions and Hepatic Glycolipid Metabolism
Jing Li, Han Yan, Rui Xiang, Weili Yang, Jingjing Ye, Ruili Yin, Jichun Yang, Yujing Chi
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH)
Xiaohan Xu, Kyle L. Poulsen, Lijuan Wu, Shan Liu, Tatsunori Miyata, Qiaoling Song, Qingda Wei, Chenyang Zhao, Chunhua Lin, Jinbo Yang
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database)
- The Effects of Glucose Lowering Agents on the Secondary Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
-
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):977-987. Published online October 14, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1046
-
-
4,015
View
-
175
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
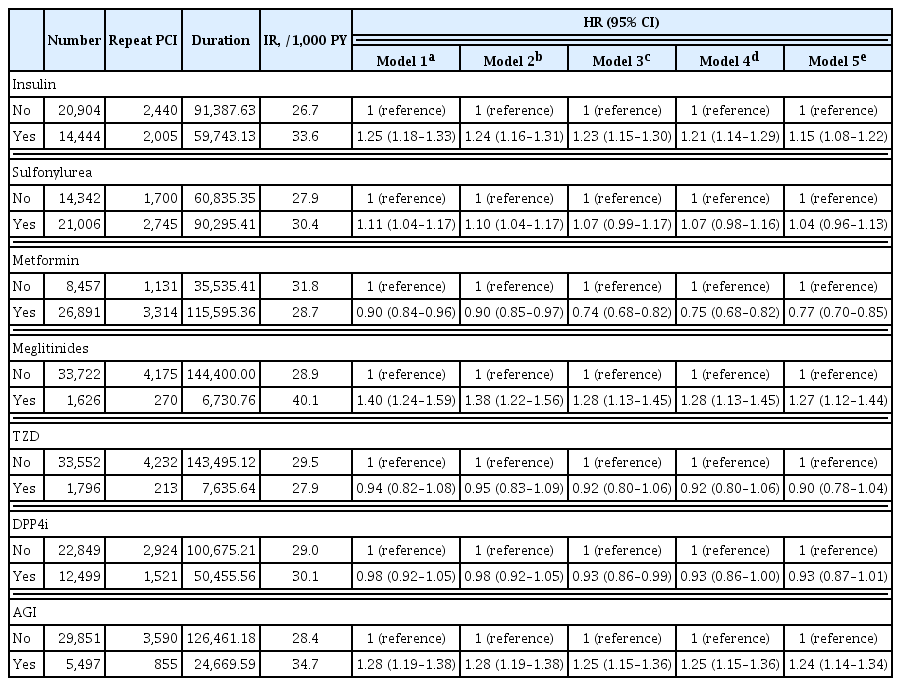
Patients with diabetes have a higher risk of requiring repeated percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) than non-diabetic patients. We aimed to evaluate and compare the effects of anti-diabetic drugs on the secondary prevention of myocardial infarction among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
We analyzed the general health check-up dataset and claims data of the Korean National Health Insurance Service of 199,714 participants (age ≥30 years) who underwent PCIs between 2010 and 2013. Those who underwent additional PCI within 1 year of their first PCI (n=3,325) and those who died within 1 year (n=1,312) were excluded. Patients were classified according to their prescription records for glucose-lowering agents. The primary endpoint was the incidence rate of coronary revascularization.
Results
A total of 35,348 patients were included in the study. Metformin significantly decreased the risk of requiring repeat PCI in all patients (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.77). In obese patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥25 kg/m2, patients treated with thiazolidinedione (TZD) exhibited a decreased risk of requiring repeat revascularization than those who were not treated with TZD (aHR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.63 to 0.95). Patients treated with metformin showed a decreased risk of requiring revascularization regardless of their BMI. Insulin, meglitinide, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor were associated with increased risk of repeated PCI.
Conclusion
The risk of requiring repeat revascularization was lower in diabetic patients treated with metformin and in obese patients treated with TZD. These results suggest that physicians should choose appropriate glucose-lowering agents for the secondary prevention of coronary artery disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Application of systemic inflammation indices and lipid metabolism-related factors in coronary artery disease
Zhuoyan Zhao, Huan Lian, Yixiang Liu, Lixian Sun, Ying Zhang
Coronary Artery Disease.2023; 34(5): 306. CrossRef - Effect of metformin on adverse outcomes in T2DM patients: Systemic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Zhicheng Xu, Haidong Zhang, Chenghui Wu, Yuxiang Zheng, Jingzhou Jiang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment of a Predictive Model for Poor Prognosis of Incomplete Revascularization in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Multivessel Disease
Huan Lian, Zhuoyan Zhao, Kelin Ma, Zhenjiang Ding, Lixian Sun, Ying Zhang
Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis.2022; 28: 107602962211392. CrossRef
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Changes in Insulin Resistance Index and the Risk of Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Diabetes: Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
-
Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Inha Jung, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1016-1028. Published online October 21, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1110
-
-
4,149
View
-
128
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
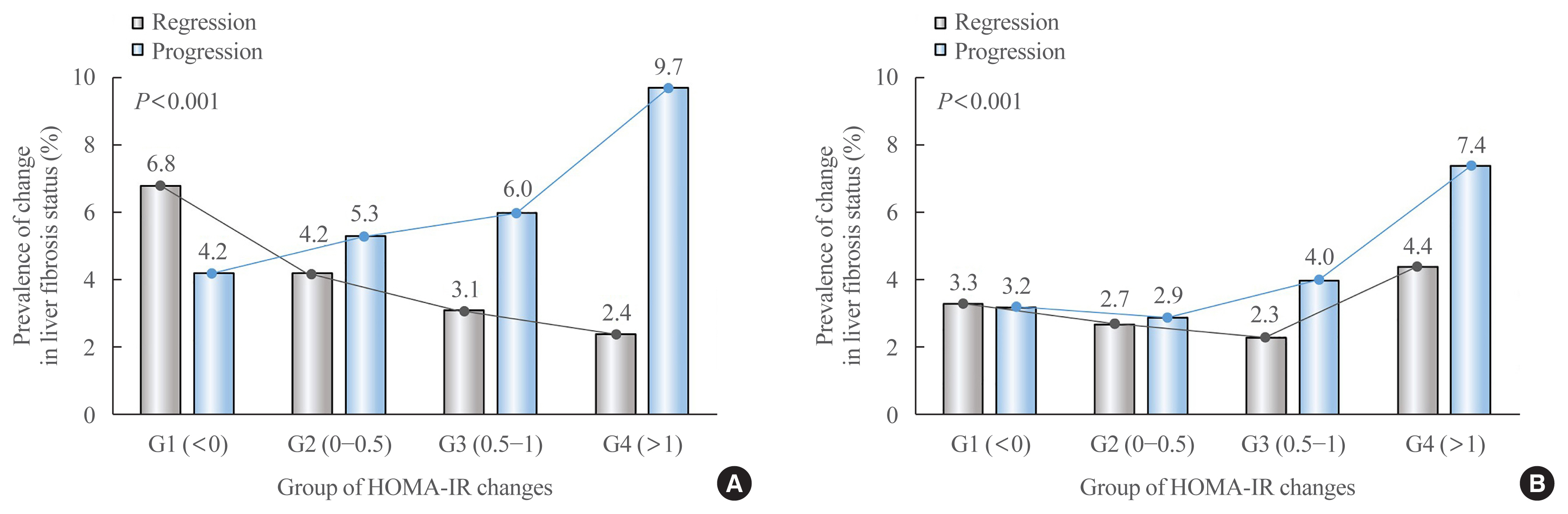
Fibrosis is the most important prognostic factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Insulin resistance plays a key role of fibrosis progression. We evaluated the association between changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) values and changes in fibrosis status in NAFLD.
Methods
We analyzed the data of 15,728 participants with NAFLD (86% men, mean age 40.5 years) who had no diabetes at baseline and visited our centers for health check-ups both in 2012 and 2016. The participants were classified into four groups according to the degree of change in HOMA-IR values from baseline to the end of follow-up: G1 (<0), G2 (0–0.50), G3 (0.51–1.00), and G4 (>1.00). NAFLD was assessed by ultrasonography, and fibrosis status was evaluated by the NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) and the aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI).
Results
After the 4-year follow-up, the multivariable-adjusted odds ratio (OR) for progression of fibrosis probability increased with increasing HOMA-IR values (OR, 2.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.87 to 2.71 for NFS; and OR, 2.55; 95% CI, 2.05 to 3.18 for APRI, G4). This tendency remained consistent throughout the subgroup analyses, except in those for female sex and a body mass index <25 kg/m2. The OR for regression of fibrosis probability decreased with increasing HOMA-IR values (OR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.43 for NFS, G4).
Conclusion
Changes in HOMA-IR values were associated with changes in fibrosis status in patients with NAFLD without diabetes, which underscores the role of insulin resistance in liver fibrosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Insulin Resistance/Sensitivity Measures as Screening Indicators of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Soodeh Jahangiri, Sohrab Nobarani, Azita Hekmatdoost, Marieh Salavatizadeh, Samira Soltanieh, Haleh Chehrehgosha, Hoda Taheri, Zeinab Montazeri, Fereshteh Attaran, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(4): 1430. CrossRef - Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: A 7-year retrospective cohort study of 3,496 adults using serial echocardiography
Gyuri Kim, Tae Yang Yu, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Cheol Bae, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; : 101534. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Yu Luo, Cuiyu Wang, Tian Zhang, Xiaoyu He, Jianan Hao, Andong Shen, Hang Zhao, Shuchun Chen, Luping Ren
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 293. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance Is Inversely Related to Incident Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Jun-Hyuk Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Kyongmin Park, Hye Sun Lee, Hoon-Ki Park, Jee Hye Han, Sang Bong Ahn
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3039. CrossRef - Machine learning models including insulin resistance indexes for predicting liver stiffness in United States population: Data from NHANES
Kexing Han, Kexuan Tan, Jiapei Shen, Yuting Gu, Zilong Wang, Jiayu He, Luyang Kang, Weijie Sun, Long Gao, Yufeng Gao
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The crosstalk between insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a culprit or a consequence?
Dae-Jeong Koo, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 132. CrossRef
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Increased Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals with High Weight Variability
-
Inha Jung, Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):845-854. Published online August 27, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1098
-
-
4,916
View
-
140
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
8
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
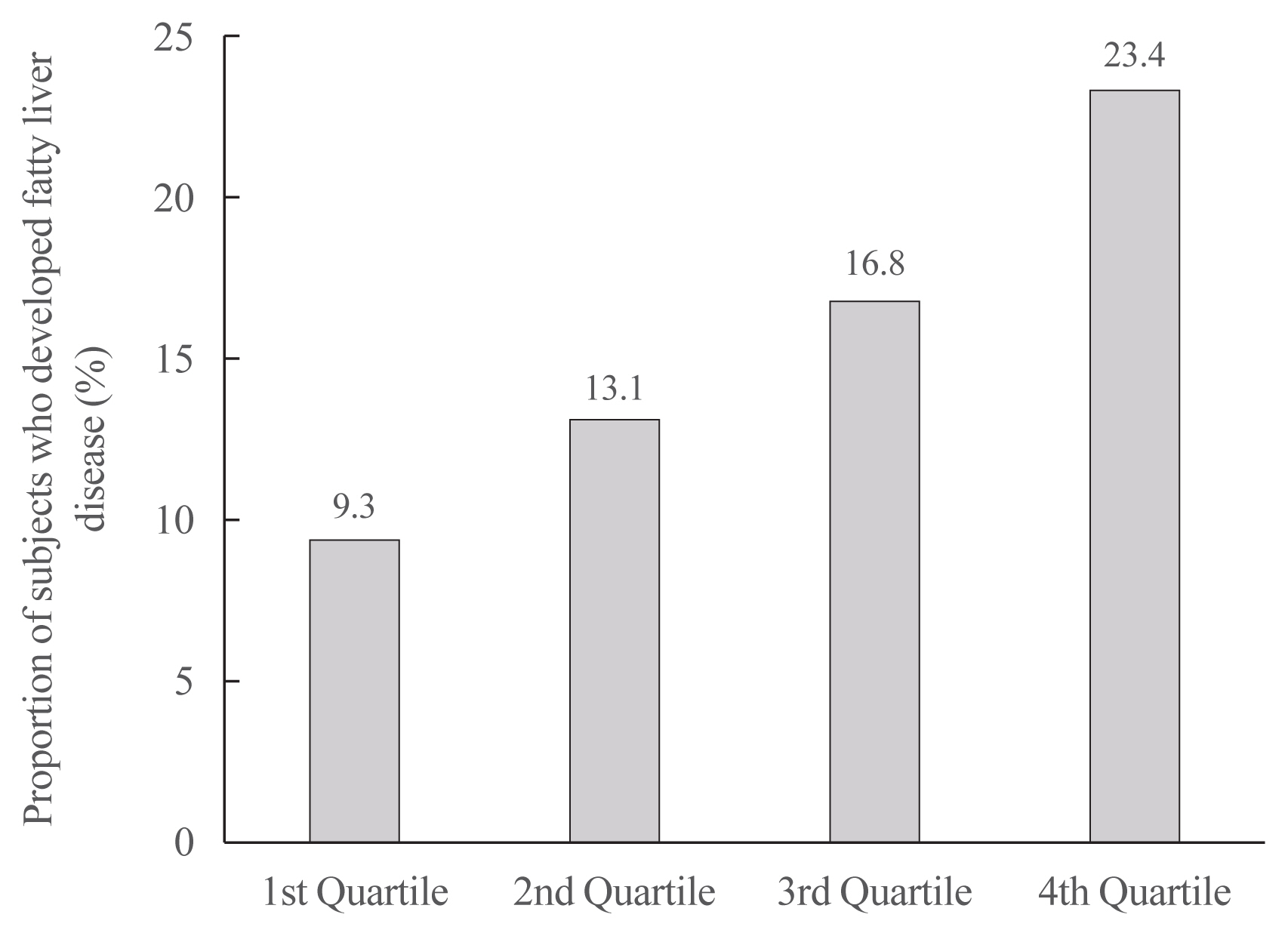
Weight loss through lifestyle modification is recommended for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent studies have suggested that repeated loss and gain of weight is associated with worse health outcomes. This study aimed to examine the association between weight variability and the risk of NAFLD in patients without diabetes.
Methods
We examined the health-checkup data of 30,708 participants who had undergone serial examinations between 2010 and 2014. Weight variability was assessed using coefficient of variation and the average successive variability of weight (ASVW), which was defined as the sum of absolute weight changes between successive years over the 5-year period divided by 4. The participants were classified according to the baseline body mass index and weight difference over 4 years.
Results
On dividing the participants into four groups according to ASVW quartile groups, those in the highest quartile showed a significantly increased risk of NAFLD compared to those in the lowest quartile (odds ratio [OR], 1.89; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.63 to 2.19). Among participants without obesity at baseline, individuals with high ASVW showed increased risk of NAFLD (OR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.61 to 2.01). Participants with increased weight over 4 years and high ASVW demonstrated higher risk of NAFLD compared to those with stable weight and low ASVW (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 4.29 to 5.53).
Conclusion
Regardless of participant baseline obesity status, high weight variability was associated with an increased risk of developing NAFLD. Our results suggest that further effort is required to minimize weight fluctuations after achieving a desirable body weight.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Changes in Macronutrients during Dieting Lead to Weight Cycling and Metabolic Complications in Mouse Model
Anouk Charlot, Anthony Bringolf, Léa Debrut, Joris Mallard, Anne-Laure Charles, Emilie Crouchet, Delphine Duteil, Bernard Geny, Joffrey Zoll
Nutrients.2024; 16(5): 646. CrossRef - Weight variability, physical functioning and incident disability in older adults
Katie J. McMenamin, Tamara B. Harris, Joshua F. Baker
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(4): 1648. CrossRef - Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 74. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease in individuals of normal weight
Mohammed Eslam, Hashem B. El-Serag, Sven Francque, Shiv K. Sarin, Lai Wei, Elisabetta Bugianesi, Jacob George
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2022; 19(10): 638. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Higher Weight Variability Could Bring You a Fatty Liver
Yeoree Yang, Jae-Hyoung Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 766. CrossRef - Autonomic Imbalance Increases the Risk for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Inha Jung, Da Young Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Hyemi Kwon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Won-Young Lee, Sung-Woo Park, Se Eun Park
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetes
- Best Achievements in Clinical Medicine in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia in 2020
-
Eun-Jung Rhee, Mee-Kyung Kim, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):41-50. Published online February 24, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.106
-
-
4,302
View
-
178
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Over the last two decades, our understanding of diabetes and treatment strategies have evolved tremendously, from scientific, mechanistic, and human perspectives. The categories of anti-diabetic medications expanded from a few to numerous, enabling clinicians to personalize diabetes care and treatment. Thanks to rapid growth in the field of science and medical engineering, newer treatment options are coming to the market with various advantages and disadvantages to be aware of. Therefore, clinicians should rapidly adopt new trends based on guidelines and data from many clinical trials in the field of diabetes. In the treatment of dyslipidemia, trends and guidelines are changing every year, and novel therapies are being developed. In this review, we would like to summarize the major achievements in clinical medicine in 2020 in the field of diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Effects of exercise initiation and smoking cessation after new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on risk of mortality and cardiovascular outcomes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Obesity and Dyslipidaemia on the Prevalence of Diabetes Amongst Adults Aged ≥45 Years: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study
Simin Zhang, Donghan Sun, Xiaoyi Qian, Li Li, Wenwen Wu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8036. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
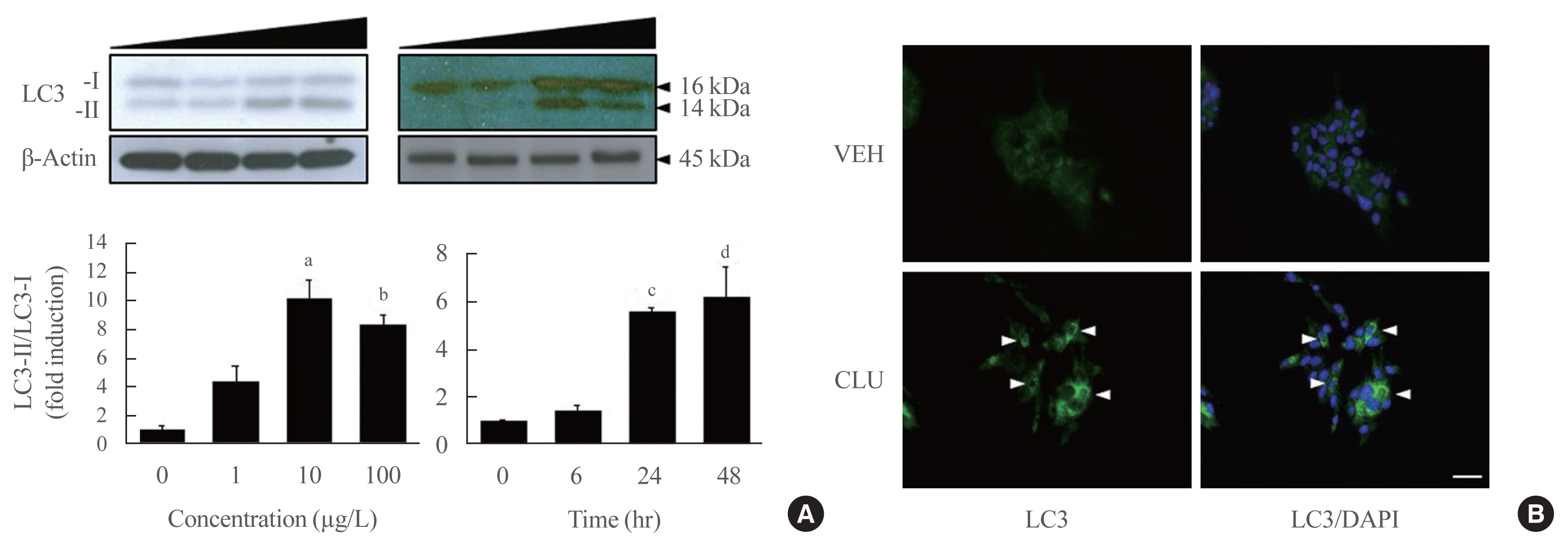
- Clusterin Protects Lipotoxicity-Induced Apoptosis via Upregulation of Autophagy in Insulin-Secreting Cells
-
Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Min Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):943-953. Published online December 2, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.768
-
-
5,662
View
-
135
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
There is a great need to discover factors that could protect pancreatic β-cells from apoptosis and thus prevent diabetes mellitus. Clusterin (CLU), a chaperone protein, plays an important role in cell protection in numerous cells and is involved in various cellular mechanisms, including autophagy. In the present study, we investigated the protective role of CLU through autophagy regulation in pancreatic β-cells.
Methods
To identify the protective role of CLU, mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells were incubated with CLU and/or free fatty acid (FFA) palmitate, and cellular apoptosis and autophagy were examined.
Results
Treatment with CLU remarkably upregulated microtubule-associated protein 1-light chain 3 (LC3)-II conversion in a doseand time-dependent manner with a significant increase in the autophagy-related 3 (Atg3) gene expression level, which is a mediator of LC3-II conversion. Moreover, co-immunoprecipitation and fluorescence microscopy experiments showed that the molecular interaction of LC3 with Atg3 and p62 was markedly increased by CLU. Stimulation of LC3-II conversion by CLU persisted in lipotoxic conditions, and FFA-induced apoptosis and dysfunction were simultaneously improved by CLU treatment. Finally, inhibition of LC3-II conversion by Atg3 gene knockdown markedly attenuated the cytoprotective effect of CLU.
Conclusion
Taken together, these findings suggest that CLU protects pancreatic β-cells against lipotoxicity-induced apoptosis via autophagy stimulation mediated by facilitating LC3-II conversion. Thus, CLU has therapeutic effects on FFA-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention to protect pancreatic beta cells in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Alexandra Coomans de Brachène, Corentin Scoubeau, Anyïshai E. Musuaya, Jose Maria Costa-Junior, Angela Castela, Julie Carpentier, Vitalie Faoro, Malgorzata Klass, Miriam Cnop, Decio L. Eizirik
Diabetologia.2023; 66(3): 450. CrossRef - Apolipoprotein J Attenuates Vascular Restenosis by Promoting Autophagy and Inhibiting the Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Ning Yang, Bo Dong, Yanqiu Song, Yang Li, Lu Kou, Qin Qin
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research.2022; 15(5): 1086. CrossRef - Targets for rescue from fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells
Seok-Woo Hong, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 57. CrossRef - Co-regulators of autophagy and the cell cycle in HFD − As treated mice
Marzieh Zeinvand-Lorestani, Mohammad Javad Khodayar, Ali Teimoori, Najmaldin Saki, Akram Ahangarpour, Ali Ranjbar, Hamed Zeinvand-Lorestani
Journal of Trace Elements and Minerals.2022; 2: 100018. CrossRef - Targeting pancreatic β cells for diabetes treatment
Chirag Jain, Ansarullah, Sara Bilekova, Heiko Lickert
Nature Metabolism.2022; 4(9): 1097. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Beta-Cell Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetes-Prone Situations and Potential Protection by GLP-1-Based Therapies
Safia Costes, Gyslaine Bertrand, Magalie A. Ravier
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(10): 5303. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
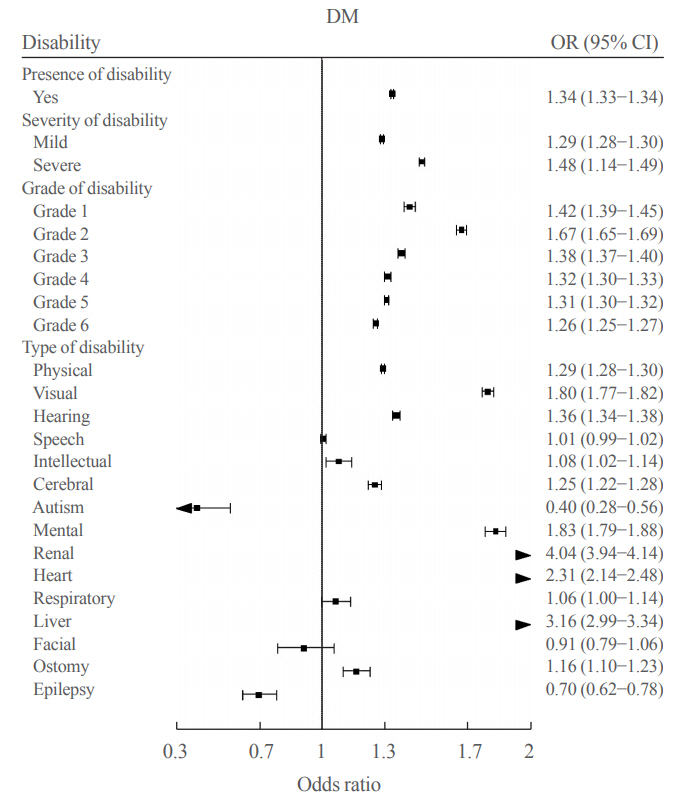
- The Prevalence and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults with Disabilities in Korea
-
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):552-561. Published online July 22, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.653
-
-
8,100
View
-
188
Download
-
11
Web of Science
-
11
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
People with disabilities are at risk of secondary conditions such as diabetes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and risk of type 2 diabetes in South Korea, especially among people with all types of disabilities.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service, with two disabilityfree controls matched for each participant with disabilities by age and sex. Information regarding the type, severity and grade of disabilities was obtained based on the National Disability Registry. Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes was defined according to the following criteria: presence of International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification codes E11, E12, E13, or E14 and claims for at least one oral anti-diabetic agent or insulin at baseline, or fasting glucose level ≥126 mg/dL.
Results
We included 1,297,806 participants with disabilities and 2,943,719 control. Out of 4,241,525 participants, 841,990 (19.9%) were diagnosed with diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes was higher in the disability group compared with individuals without disabilities (23.1% vs. 18.4%). The odds of having diabetes was higher in the disability group compared with the control group (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.33 to 1.34). The results showed higher prevalence of diabetes in the mildly disabled group (23.2%) than in the severely disabled group (22.7%).
Conclusion
The prevalence and risk of diabetes were higher in people with disabilities compared with the general population. Physicians and public health authorities should focus on people with disabilities for proper diabetes management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - Bipolar disorder and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, heart failure, and all-cause mortality: a population-based matched cohort study in South Korea
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychotic Disorders and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases, and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Matched Cohort Study
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 122. CrossRef - Pathways linking health literacy to self-care in diabetic patients with physical disabilities: A moderated mediation model
Hye Jin Nam, Ju Young Yoon, Wen-Jun Tu
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(3): e0299971. CrossRef - Dysphagia Requiring Medical Attention in Parkinson’s Disease: A Korean Population-Based Study
Seungwoo Cha, Won Kee Chang, Hee-Mun Cho, Kyungdo Han, Nam-Jong Paik, Sohyun Kwon, Won-Seok Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Disparities in diabetes-related avoidable hospitalization among diabetes patients with disability using a nationwide cohort study
Hin Moi Youn, Dong-Woo Choi, Sung-In Jang, Eun-Cheol Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Disability type–specific mortality patterns and life expectancy among disabled people in South Korea using 10-year combined data between 2008 and 2017
Jinwook Bahk, Hee-Yeon Kang, Young-Ho Khang
Preventive Medicine Reports.2022; 29: 101958. CrossRef - Cholecystectomy reduces the risk of myocardial and cerebral infarction in patients with gallstone-related infection
Seon Mee Park, Hyun Jung Kim, Tae Uk Kang, Heather Swan, Hyeong Sik Ahn
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nationwide trends in the incidence of tuberculosis among people with disabilities in Korea:
a nationwide serial cross-sectional study
Jinsoo Min, So Young Kim, Jong Eun Park, Yeon Yong Kim, Jong Hyock Park
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022098. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and future risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eun Sil Koh, Oak-Kee Hong, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108799. CrossRef - Diabetes in People with Disabilities: a Call for Action
Inha Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(4): 82. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
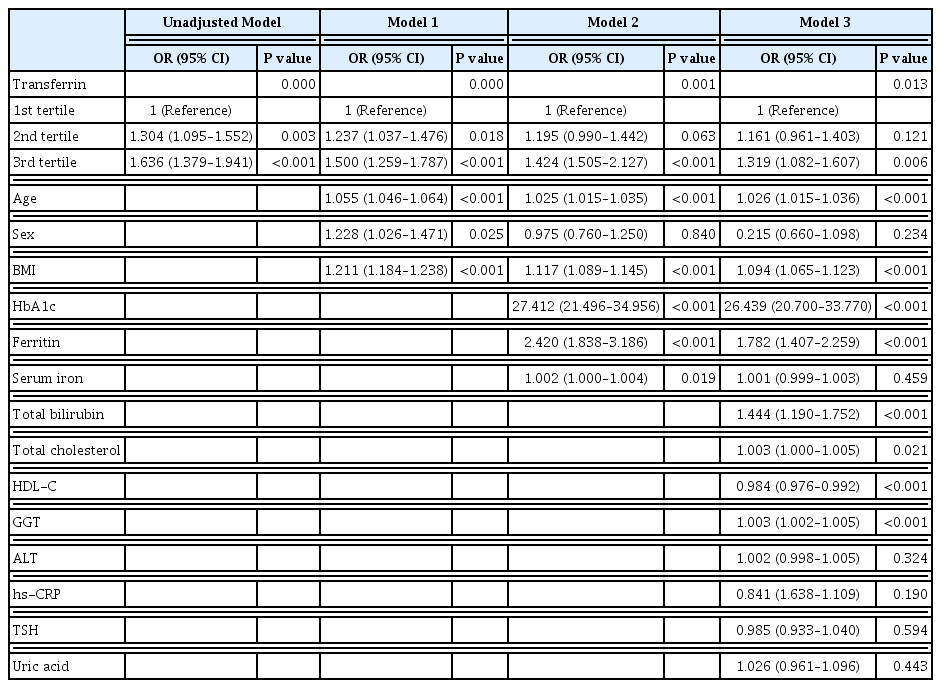
- Serum Transferrin Predicts New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
-
Jong Dai Kim, Dong-Mee Lim, Keun-Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):610-617. Published online September 22, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.721
-
-
4,393
View
-
98
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
It is well known that high serum ferritin, a marker of iron storage, predicts incident type 2 diabetes. Limited information is available on the association between transferrin, another marker of iron metabolism, and type 2 diabetes. Thus, we investigated the association between transferrin and incident type 2 diabetes.
Methods
Total 31,717 participants (mean age, 40.4±7.2 years) in a health screening program in 2005 were assessed via cross-sectional analysis. We included 30,699 subjects who underwent medical check-up in 2005 and 2009 and did not have type 2 diabetes at baseline in this retrospective longitudinal analysis.
Results
The serum transferrin level was higher in the type 2 diabetes group than in the non-type 2 diabetes group (58.32±7.74 μmol/L vs. 56.17±7.96 μmol/L, P<0.001). Transferrin correlated with fasting serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in the correlational analysis (r=0.062, P<0.001 and r=0.077, P<0.001, respectively) after full adjustment for covariates. Transferrin was more closely related to homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance than to homeostasis model assessment of β cell function (r=0.042, P<0.001 and r=–0.019, P=0.004, respectively) after full adjustment. Transferrin predicted incident type 2 diabetes in non-type 2 diabetic subjects in a multivariate linear regression analysis; the odds ratio (95% confidence interval [CI]) of the 3rd tertile compared to that in the 1st tertile of transferrin for incident diabetes was 1.319 (95% CI, 1.082 to 1.607) after full adjustment (P=0.006).
Conclusion
Transferrin is positively associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes
Xingyue Wang, You Wang, Junjie Hou, Hongyang Liu, Rong Zeng, Xiangyu Li, Mei Han, Qingrun Li, Linong Ji, Desi Pan, Weiping Jia, Wen Zhong, Tao Xu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Proteomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer in Patients with Diabetes
Muhammad Mujammami, Mohamed Rafiullah, Khalid Akkour, Assim A. Alfadda, Afshan Masood, Salini Scaria Joy, Hani Alhalal, Maria Arafah, Eman Alshehri, Ibrahim O. Alanazi, Hicham Benabdelkamel
ACS Omega.2024; 9(4): 4721. CrossRef - Association between systemic iron status and β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Yao Qin, Yiting Huang, Yuxiao Li, Lu Qin, Qianying Wei, Xin Chen, Chuanhui Yang, Mei Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Serum Level of Ceruloplasmin, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Transferrin as Markers of Severity in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Patricia-Andrada Reștea, Ștefan Țigan, Laura Grațiela Vicaș, Luminița Fritea, Eleonora Marian, Tunde Jurca, Annamaria Pallag, Iulius Liviu Mureșan, Corina Moisa, Otilia Micle, Mariana Eugenia Mureșan
Microbiology Research.2023; 14(4): 1670. CrossRef
- Miscellaneous
- Encountering COVID-19 as Endocrinologists
-
Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung Hee Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):197-205. Published online June 23, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.197
-
-
13,293
View
-
277
Download
-
13
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- The world is entering an era of disaster and chaos due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Since its first emergence in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, COVID-19 has swept through Asia and propagated throughout the world to Europe and North America. As of April 13, 1,773,084 people were infected and 111,652 people had died from COVID-19 globally, and new record levels of infection are being reported every day. Based on the data that have been amassed so far, the primary risk factors for a severe disease course or even mortality from COVID-19 are underlying diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to increase, patients with endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus and those who are on long-term corticosteroid therapy due to adrenal insufficiency or hypopituitarism are at risk for a poor prognosis of COVID-19. As endocrinologists, we would like to briefly review the current knowledge about the relationship between COVID-19 and endocrine diseases and to discuss what we can do for the safety and health of our patients with endocrine diseases in this globally threatening situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Adverse Events Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents with Endocrinological Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study
İbrahim Mert Erbaş, İrem Ceren Erbaş, Gözde Akın Kağızmanlı, Kübra Yüksek Acinikli, Özge Besci, Korcan Demir, Ece Böber, Nurşen Belet, Ayhan Abacı
Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology.2023; 15(3): 248. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - New-onset and relapsed Graves’ disease following COVID-19 vaccination: a comprehensive review of reported cases
Kan Chen, Yiyang Gao, Jing Li
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Neuroendocrine Changes and Hypothalamo-Pituitary
Autoimmunity in Patients with COVID-19
Mustafa Sait Gonen, Annamaria De Bellis, Emre Durcan, Giuseppe Bellastella, Paolo Cirillo, Lorenzo Scappaticcio, Miriam Longo, Basak Ecem Bircan, Serdar Sahin, Cem Sulu, Hande Mefkure Ozkaya, Dildar Konukoglu, Fatma Ferda Kartufan, Fahrettin Kelestimur
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2022; 54(03): 153. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Association intensify risk factors for morbidity and mortality
Prateek Sharma, Tapan Behl, Neelam Sharma, Sukhbir Singh, Ajmer Singh Grewal, Ali Albarrati, Mohammed Albratty, Abdulkarim M. Meraya, Simona Bungau
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 151: 113089. CrossRef - The Relationship between COVID-19 and Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis: A Large Spectrum from Glucocorticoid Insufficiency to Excess—The CAPISCO International Expert Panel
Mojca Jensterle, Rok Herman, Andrej Janež, Wael Al Mahmeed, Khalid Al-Rasadi, Kamila Al-Alawi, Maciej Banach, Yajnavalka Banerjee, Antonio Ceriello, Mustafa Cesur, Francesco Cosentino, Massimo Galia, Su-Yen Goh, Sanjay Kalra, Peter Kempler, Nader Lessan,
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(13): 7326. CrossRef - WhatsApp-Based virtual consultation in clinical practice during COVID times: A prospective institutional study
RamakanthBhargav Panchangam, Pradeep Puthenveetil, SunilKumar Kota, Sabaretnam Mayilvaganan
Annals of African Medicine.2022; 21(2): 132. CrossRef - Thyroid and COVID-19: a review on pathophysiological, clinical and organizational aspects
G. Lisco, A. De Tullio, E. Jirillo, V. A. Giagulli, G. De Pergola, E. Guastamacchia, V. Triggiani
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(9): 1801. CrossRef - Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeongwoo Lee, Hyewon Nam, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Dong Wook Shin, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 251. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - Collateral Damage of the COVID‐19 Pandemic on Nutritional Quality and Physical Activity: Perspective from South Korea
Soo Lim, Hyunjung Lim, Jean‐Pierre Després
Obesity.2020; 28(10): 1788. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 in the post-acute phase patients - possible links with physical and rehabilitation medicine and balneotherapy
Constantin Munteanu, Diana-Loreta PĂUN, Alina-Maria ȘUȚĂ, Simin Aysel FLORESCU, Gelu ONOSE, Mihail Hoteteu
Balneo Research Journal.2020; 11(Vol.11, no): 350. CrossRef - Managing Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic
John Doupis, Konstantinos Avramidis
European Endocrinology.2020; 16(2): 85. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 737. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and the Endocrine System
Michelle D Lundholm, Caroline Poku, Nicholas Emanuele, Mary Ann Emanuele, Norma Lopez
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Study
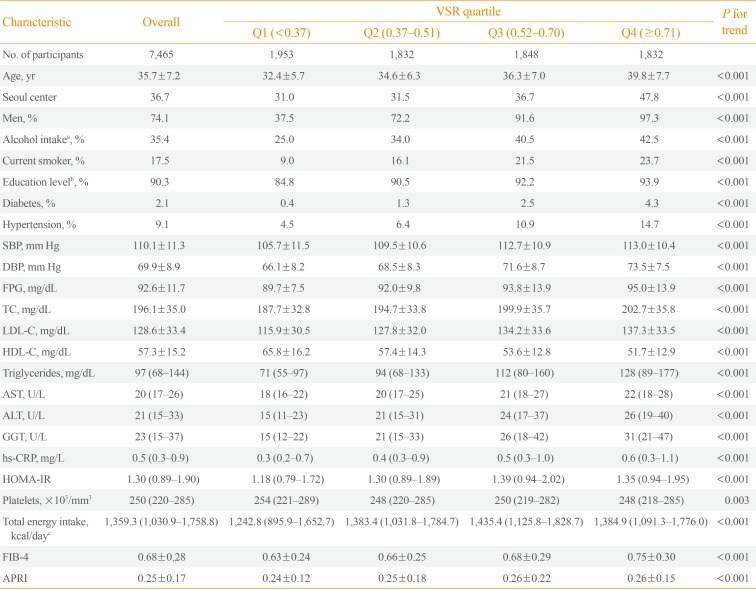
- Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat Ratio Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
-
Chan-Hee Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):165-176. Published online March 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.165
-
-
6,520
View
-
137
Download
-
26
Web of Science
-
27
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
We evaluated the association of visceral-to-subcutaneous fat ratio (VSR) with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and advanced fibrosis degree based on noninvasive serum fibrosis markers in the general population with NAFLD. MethodsThis is a cross-sectional study, in 7,465 Korean adults who underwent health screening examinations. NAFLD was defined as fatty liver detected on ultrasonography, and visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat was measured using computed tomography. We predicted fibrosis based on the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score and aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI) and categorized the risk for advanced fibrosis as low, indeterminate, or high. ResultsThe multivariable-adjusted prevalence ratios for indeterminate to high risk of advanced fibrosis based on FIB-4, determined by comparing the second, third, and fourth quartiles with the first quartile of VSR, were 3.38 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.64 to 17.97), 9.41 (95% CI, 1.97 to 45.01), and 19.34 (95% CI, 4.06 to 92.18), respectively. The multivariable-adjusted prevalence ratios for intermediate to high degree of fibrosis according to APRI also increased across VSR quartiles (5.04 [95% CI, 2.65 to 9.59], 7.51 [95% CI, 3.91 to 14.42], and 19.55 [95% CI, 9.97 to 38.34], respectively). High VSR was more strongly associated with the prevalence of NAFLD in nonobese subjects than in obese subjects, and the associations between VSR and intermediate to high probability of advanced fibrosis in NAFLD were stronger in obese subjects than in nonobese subjects. ConclusionHigh VSR values predicted increased NAFLD risk and advanced fibrosis risk with NAFLD, and the predictive value of VSR for indeterminate to high risk of advanced fibrosis was higher in obese subjects than in nonobese subjects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Opportunistic Extraction of Quantitative CT Biomarkers: Turning the Incidental Into Prognostic Information
Mohammad Nazri Md Shah, Raja Rizal Azman, Wai Yee Chan, Kwan Hoong Ng
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal.2024; 75(1): 92. CrossRef - Positive Association Between the Chinese Visceral Adiposity Index and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean Adults
Shuxia Shen, Hangkai Huang, Jinghua Wang, Zexi Tang, Chao Shen, Chengfu Xu
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2023; 68(2): 656. CrossRef - Association between Sarcopenic Obesity Status and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Fibrosis
Wolhwa Song, Sung Hwan Yoo, Jinsun Jang, Su Jung Baik, Byoung Kwon Lee, Hyun Woong Lee, Jong Suk Park
Gut and Liver.2023; 17(1): 130. CrossRef - Using hyperhomocysteinemia and body composition to predict the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in healthcare workers
Xiaoyan Hao, Honghai He, Liyuan Tao, Peng Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral and subcutaneous fat, muscle mass, and liver volume as noninvasive predictors of the progress of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Omar M. Mahmoud, Gehad Abd Elaziz Mahmoud, Haisam Atta, Wael A. Abbas, Hanan M. Ahmed, Mohamed A. A. Abozaid
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between metabolic associated fatty liver disease and body fat ratio, visceral fat area, and resting metabolic rate estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis
Deng-Hua He, Yong-Zhan Zhang, Liang Xu, Jia-Jia Pei, Ying Zhang, Zhong-Fang Yan
World Chinese Journal of Digestology.2023; 31(2): 56. CrossRef - Poor glycaemic control and ectopic fat deposition mediates the increased risk of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in high-risk populations with type 2 diabetes: Insights from Bayesian-network modelling
T. Waddell, A. Namburete, P. Duckworth, A. Fichera, A. Telford, H. Thomaides-Brears, D. J. Cuthbertson, M. Brady
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 220. CrossRef - Subcutaneous Fat Obesity in a High Body Mass Index Donor Is Not a Contraindication to Living Donor Hepatectomy
Hirak Pahari, Amey Sonavane, Amruth Raj, Anup Kumar Agrawal, Ambreen Sawant, Deepak Kumar Gupta, Amit Gharat, Vikram Raut, Sorabh Kapoor
Case Reports in Hepatology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of cardiometabolic risk factors between obese and non-obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Zahra Yari, Danial Fotros, Azita Hekmatdoost
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Radiographic Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Ratio in Patients with Cirrhosis
Nghiem B. Ha, Soo-Jin Cho, Yara Mohamad, Dorothea Kent, Grace Jun, Randi Wong, Vivek Swarnakar, Shezhang Lin, Jacquelyn J. Maher, Jennifer C. Lai
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2022; 67(7): 3436. CrossRef - The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - The effect of combined exercises on the plasma levels of retinol-binding protein 4 and its relationship with insulin resistance and hepatic fat content in postmenopausal women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Masoumeh NOROUZPOUR, Sayyed M. MARANDI, Mohsen GHANBARZADEH, Abbasali ZARE MAIVAN
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Perirenal Fat Thickness Was Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yuxian Yang, Shuting Li, Yuechao Xu, Jing Ke, Dong Zhao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1505. CrossRef - Visceral adiposity is an independent risk factor for high intra-operative blood loss during living-donor liver transplantation; could preoperative rehabilitation and nutritional therapy mitigate that risk?
Mahmoud Macshut, Toshimi Kaido, Siyuan Yao, Yosuke Miyachi, Mohamed Sharshar, Sena Iwamura, Masaaki Hirata, Hisaya Shirai, Naoko Kamo, Shintaro Yagi, Shinji Uemoto
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(3): 956. CrossRef - A review of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in non‐obese and lean individuals
Mitra Ahadi, Kasra Molooghi, Negin Masoudifar, Ali Beheshti Namdar, Hassan Vossoughinia, Mohammadreza Farzanehfar
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(6): 1497. CrossRef - Quantification of abdominal fat from computed tomography using deep learning and its association with electronic health records in an academic biobank
Matthew T MacLean, Qasim Jehangir, Marijana Vujkovic, Yi-An Ko, Harold Litt, Arijitt Borthakur, Hersh Sagreiya, Mark Rosen, David A Mankoff, Mitchell D Schnall, Haochang Shou, Julio Chirinos, Scott M Damrauer, Drew A Torigian, Rotonya Carr, Daniel J Rader
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.2021; 28(6): 1178. CrossRef - Hepatic Steatosis in Patients With Single Ventricle and a Fontan Circulation
David A. Katz, Daniel Peck, Adam M. Lubert, Mathias Possner, Faizeen Zafar, Andrew T. Trout, Joseph J. Palermo, Nadeem Anwar, Jonathan R. Dillman, Adam W. Powell, Stavra A. Xanthakos, Alexander R. Opotowsky, Gruschen Veldtman, Tarek Alsaied
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Superficial vs Deep Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue: Sex-Specific Associations With Hepatic Steatosis and Metabolic Traits
Tessa Brand, Inge Christina Lamberta van den Munckhof, Marinette van der Graaf, Kiki Schraa, Helena Maria Dekker, Leonardus Antonius Bernardus Joosten, Mihai Gheorghe Netea, Niels Peter Riksen, Jacqueline de Graaf, Joseph Henricus Wilhelmus Rutten
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(10): e3881. CrossRef - Baseline homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance associated with fibrosis progression in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease without diabetes: A cohort study
Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Inha Jung, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Ming-Lung Yu
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0255535. CrossRef - Randomised clinical trial: semaglutide versus placebo reduced liver steatosis but not liver stiffness in subjects with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by magnetic resonance imaging
Anne Flint, Grit Andersen, Paul Hockings, Lars Johansson, Anni Morsing, Mads Sundby Palle, Thomas Vogl, Rohit Loomba, Leona Plum‐Mörschel
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2021; 54(9): 1150. CrossRef - Effects of IL-33 on 3T3-L1 cells and obese mice models induced by a high-fat diet
Yue Kai, Jingtao Gao, Hu Liu, Yubing Wang, Chenrui Tian, Sheng Guo, Ling He, Min Li, Zhongwei Tian, Xiangfeng Song
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 101: 108209. CrossRef - Lipid Accumulation Product as an Index for Visceral Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk among a Sample of Obese Egyptian Women
Nayera E. Hassan, Sahar A. El-Masry, Gamila S. M. El-Saeed, Mohamed S. El Hussieny
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(B): 1229. CrossRef - Combined Effects of Dyslipidemia and High Adiposity on the Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in a Middle-Aged Chinese Population
Xichang Wang, Haoyu Wang, Jiashu Li, Xiaotong Gao, Yutong Han, Weiping Teng, Zhongyan Shan, Yaxin Lai
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4513. CrossRef - Determination of “indeterminate score” measurements in lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients from western Saudi Arabia
Yasir Mohammed Khayyat
World Journal of Hepatology.2021; 13(12): 2150. CrossRef - Utility of Liver Function Tests and Fatty Liver Index to Categorize Metabolic Phenotypes in a Mediterranean Population
Dariusz Narankiewicz, Josefina Ruiz-Nava, Veronica Buonaiuto, María Isabel Ruiz-Moreno, María Dolores López-Carmona, Luis Miguel Pérez-Belmonte, Ricardo Gómez-Huelgas, María Rosa Bernal-López
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(10): 3518. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Short-Term Effects of Beraprost Sodium on the Markers for Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Microalbuminuria
-
Yun Mi Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyung Mook Choi, Won-Young Lee, Eun-Gyoung Hong
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):398-405. Published online December 23, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.398
-
-
5,301
View
-
60
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
To evaluate the changes in cardiovascular risk markers including pulse wave velocity (PWV), microalbuminuria, inflammatory cytokines, and adhesion molecules after treatment with beraprost sodium (BPS) in patients with diabetic nephropathy. MethodsThis was a multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with microalbuminuria were included. The primary endpoints were changes in microalbuminuria in spot urine and PWV after BPS or placebo (PCB) treatment for 24 weeks. The secondary endpoints were changes in clinical and metabolic parameters. ResultsA total of 52 patients completed the 24-week trial. Changes in PWV were not different significantly in the BPS and PCB groups (right, P=0.16; left, P=0.11). Changes in microalbuminuria were 14.2±157.0 and 34.5±146.6 (µg/mg Cr) in the BPS and PCB groups, respectively (P=0.63). Subgroup analysis in the high blood pressure (BP) group (baseline systolic BP >120 mm Hg and diastolic BP >80 mm Hg), showed that microalbuminuria decreased by −47.6 in the BPS group compared with an increase by 116.4 (µg/mg Cr) in the PCB group (P=0.04). Also, in the large waist circumference group (>95 cm), microalbuminuria decreased significantly in the BPS group (P=0.04). ConclusionShort-term treatment of BPS for patients with diabetic nephropathy did not show significant improvement in various cardiovascular risk factors. However, BPS significantly decreased microalbuminuria in study subjects with higher cardiovascular risk such as high BP or large waist circumference.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical efficacy of beraprost sodium in treating chronic kidney disease: A six-month prospective study
Chen Sun, Xin Wu, Xin Zhang, Shulin Li, Ruoyu Jia, Dong Sun
Heliyon.2024; 10(2): e24156. CrossRef - Clinical efficacy and safety of beraprost sodium in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome: A meta-analysis
Peng Yan, Ben Ke, Xiangdong Fang
Medicine.2023; 102(42): e34958. CrossRef - Dysregulated coagulation system links to inflammation in diabetic kidney disease
Mengyun Xiao, Donge Tang, Shaodong Luan, Bo Hu, Wenyu Gong, Wolfgang Pommer, Yong Dai, Lianghong Yin
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and cardiometabolic profile in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Peyman Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, Reza Tabrizi, Kamran Hessami, Mojtaba Shabani-Borujeni, Mahnaz Hosseini-Bensenjan, Shahla Rezaei, Mohammad Jalali, Pedram Keshavarz, Fariba Ahmadizar
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 54(1): 111. CrossRef - Thrombocytopenia in COVID‑19 and vaccine‑induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Styliani Geronikolou, Işil Takan, Athanasia Pavlopoulou, Marina Mantzourani, George Chrousos
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Platelets in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Ukhti Jamil Rustiasari, Joris J. Roelofs
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8270. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
- Deficiency of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Reduces the Expression of Prohibitin and Causes β-Cell Impairment via Mitochondrial Dysregulation
-
Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):403-412. Published online September 18, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.403
-
-
4,204
View
-
50
Download
-
16
Web of Science
-
16
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Emerging evidence suggests that sphingolipids may be involved in type 2 diabetes. However, the exact signaling defect through which disordered sphingolipid metabolism induces β-cell dysfunction remains unknown. The current study demonstrated that sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), the product of sphingosine kinase (SphK), is an essential factor for maintaining β-cell function and survival via regulation of mitochondrial action, as mediated by prohibitin (PHB). MethodsWe examined β-cell function and viability, as measured by mitochondrial function, in mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells in response to manipulation of cellular S1P and PHB levels. ResultsLack of S1P induced by sphingosine kinase inhibitor (SphKi) treatment caused β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis, with repression of mitochondrial function shown by decreases in cellular adenosine triphosphate content, the oxygen consumption rate, the expression of oxidative phosphorylation complexes, the mitochondrial membrane potential, and the expression of key regulators of mitochondrial dynamics (mitochondrial dynamin-like GTPase [OPA1] and mitofusin 1 [MFN1]). Supplementation of S1P led to the recovery of mitochondrial function and greatly improved β-cell function and viability. Knockdown of SphK2 using small interfering RNA induced mitochondrial dysfunction, decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS), and reduced the expression of PHB, an essential regulator of mitochondrial metabolism. PHB deficiency significantly reduced GSIS and induced mitochondrial dysfunction, and co-treatment with S1P did not reverse these trends. ConclusionAltogether, these data suggest that S1P is an essential factor in the maintenance of β-cell function and survival through its regulation of mitochondrial action and PHB expression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mitochondrial Cristae Morphology Reflecting Metabolism, Superoxide Formation, Redox Homeostasis, and Pathology
Petr Ježek, Martin Jabůrek, Blanka Holendová, Hana Engstová, Andrea Dlasková
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2023; 39(10-12): 635. CrossRef - Sphingolipids in mitochondria—from function to disease
Maryam Jamil, Lauren Ashley Cowart
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine‐1‐phosphate in mitochondrial function and metabolic diseases
Meng Duan, Pan Gao, Sheng‐xi Chen, Petr Novák, Kai Yin, Xiao Zhu
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Involvement of miR‐27a‐3p in diabetic nephropathy via affecting renal fibrosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Lina Wu, Qingzhu Wang, Feng Guo, Xiaojun Ma, Jiao Wang, Yanyan Zhao, Yushan Yan, Guijun Qin
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2021; 236(2): 1454. CrossRef - Sphingosine‐1‐phosphate in acute exercise and training
Katarzyna Hodun, Adrian Chabowski, Marcin Baranowski
Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports.2021; 31(5): 945. CrossRef - The Ethyl Acetate Extract From Celastrus orbiculatus Promotes Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Mitochondria Regulation by PHB
Lide Tao, Zixin Yin, Tengyang Ni, Zewen Chu, Shihua Hao, Zeyu Wang, Masataka Sunagawa, Haibo Wang, Yanqing Liu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine 1-phosphate Stimulates Insulin Secretion and Improves Cell Survival by Blocking Voltage-dependent K+ Channels in β Cells
Zhihong Liu, Huanhuan Yang, Linping Zhi, Huan Xue, Zhihong Lu, Yanli Zhao, Lijuan Cui, Tao Liu, Shouan Ren, Peifeng He, Yunfeng Liu, Yi Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine-1 Phosphate Lyase Regulates Sensitivity of Pancreatic Beta-Cells to Lipotoxicity
Yadi Tang, Thomas Plötz, Markus H. Gräler, Ewa Gurgul-Convey
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10893. CrossRef - Sphingolipids and Mitochondrial Dynamic
Lais Brigliadori Fugio, Fernanda B. Coeli-Lacchini, Andréia Machado Leopoldino
Cells.2020; 9(3): 581. CrossRef - Diminished Sphingolipid Metabolism, a Hallmark of Future Type 2 Diabetes Pathogenesis, Is Linked to Pancreatic β Cell Dysfunction
Saifur R. Khan, Yousef Manialawy, Andreea Obersterescu, Brian J. Cox, Erica P. Gunderson, Michael B. Wheeler
iScience.2020; 23(10): 101566. CrossRef - Neuronal Metabolism and Neuroprotection: Neuroprotective Effect of Fingolimod on Menadione-Induced Mitochondrial Damage
Antonio Gil, Elisa Martín-Montañez, Nadia Valverde, Estrella Lara, Federica Boraldi, Silvia Claros, Silvana-Yanina Romero-Zerbo, Oscar Fernández, Jose Pavia, Maria Garcia-Fernandez
Cells.2020; 10(1): 34. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Ceramide and Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in adipose dysfunction
Zijian Fang, Susan Pyne, Nigel J. Pyne
Progress in Lipid Research.2019; : 100991. CrossRef - Dynamic of mitochondrial network, cristae, and mitochondrial nucleoids in pancreatic β-cells
Petr Ježek, Andrea Dlasková
Mitochondrion.2019; 49: 245. CrossRef - Sphingosine kinase 1 overexpression induces MFN2 fragmentation and alters mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ handling in HeLa cells
I. Pulli, C. Löf, T. Blom, M.Y. Asghar, T. Lassila, N. Bäck, K.-L. Lin, J.H. Nyström, K. Kemppainen, D.M. Toivola, E. Dufour, A. Sanz, H.M. Cooper, J.B. Parys, K. Törnquist
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2019; 1866(9): 1475. CrossRef - Ceramide and sphingosine 1-phosphate in adipose dysfunction
Zijian Fang, Susan Pyne, Nigel J. Pyne
Progress in Lipid Research.2019; 74: 145. CrossRef - S1P/S1P Receptor Signaling in Neuromuscolar Disorders
Elisabetta Meacci, Mercedes Garcia-Gil
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(24): 6364. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Prevalence and Annual Incidence of Thyroid Disease in Korea from 2006 to 2015: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
-
Hyemi Kwon, Jin-hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Ji Min Han, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):260-267. Published online June 21, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.260
-
-
6,406
View
-
128
Download
-
37
Web of Science
-
37
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The incidence of thyroid nodules has increased worldwide in recent years. Thyroid dysfunction is a potential risk factor for hypercholesterolemia, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, arrhythmia, and neuropsychiatric disease. This study investigated the prevalence and annual incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism in Koreans. MethodsIn this nationwide population-based cohort study, 51,834,660 subjects were included using the National Health Information database from 2006 to 2015, after the exclusion of subjects with thyroid cancer. ResultsThe prevalence in Korea in 2015 of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism in patients taking thyroid hormone, and hyperthyroidism in patients undergoing treatment was 15.82/1,000 population, 15.94/1,000 population, and 2.76/1,000 population, respectively. All these diseases were more prevalent among women than among men. The number of incident cases of these three thyroid diseases steadily increased from 2006 to 2012, and then decreased through 2015. The incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism treated with thyroid hormone, and treated hyperthyroidism was 6.79/1,000 population, 1.76/1,000 population, and 0.55/1,000 population, respectively, in Korea in 2015. The use of methimazole continuously increased, from 33% of total antithyroid drug prescriptions in 2006 to 74.4% in 2015, and it became the most frequently prescribed antithyroid drug in Korea. In contrast, the use of propylthiouracil continuously decreased. ConclusionThis was the first nationwide study of the prevalence and annual incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism to take into account recent changes and to include the current status of patients receiving treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - New-onset atrial fibrillation in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: association with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs treatment
Hyung Woo Kim, Minkyung Han, Inkyung Jung, Sung Soo Ahn
Rheumatology.2024; 63(3): 630. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer Among Young Adults in South Korea
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Sun Joon Moon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1095. CrossRef - Endocrine and metabolic comorbidities in primary cicatricial alopecia: A nationwide population‐based study
Da‐Ae Yu, Seong Rae Kim, Soo Ick Cho, Ohsang Kwon
The Journal of Dermatology.2024; 51(3): 429. CrossRef - Risk of non-thyroidal autoimmune diseases in patients with Graves’ disease: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Seo Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Ji-Won Kwon, Ji-Min Kweon, Ju-Yeun Lee
Rheumatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Risk in Graves Disease with Radioactive131I Treatment: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Kyoung Jin Kim, Eyun Song, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim
Journal of Nuclear Medicine.2024; : jnumed.123.266531. CrossRef - Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients
Jung-Chi Hsu, Kang-Chih Fan, Ting-Chuan Wang, Shu-Lin Chuang, Ying-Ting Chao, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Lian-Yu Lin, Lung-Chun Lin
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Myotonic dystrophy type 1 in South Korea: a comprehensive analysis of cancer and comorbidity risks
Incheol Seo, Jin-Mo Park
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of ITM2A rs1751094 polymorphism on X chromosome in Korean pediatric patients with autoimmune thyroid disease
Won K. Cho, In‐Cheol Baek, Sung E. Kim, Mirae Kim, Tai‐Gyu Kim, Byung‐Kyu Suh
Immunity, Inflammation and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Risk Stratification of Follicular-patterned Thyroid Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy by Histologic Subtyping and RAS Variant-specific Immunohistochemistry
Meejeong Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(2): 247. CrossRef - Cancer and Mortality Risks of Graves’ Disease in South Korea Based on National Data from 2010 to 2019
Young Ju Choi, Kyungdo Han, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Byung-Kyu Suh
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 535. CrossRef - Acromegaly and the long-term fracture risk of the vertebra and hip: a national cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Bong-Sung Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(9): 1591. CrossRef - Association of Thyroid Hormone Medication Adherence With Risk of Dementia
Saemi Han, Seogsong Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Sun Jae Park, Kyae Hyung Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Yoosun Cho, Joung Sik Son, Sang Min Park
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e225. CrossRef - Increased risk of incident gout in patients with hyperthyroidism: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Ju-Yeun Lee, So-Yeon Park, Seo Young Sohn
Rheumatology International.2023; 44(3): 451. CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 436. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of chemokine gene polymorphisms in Korean children with autoimmune thyroid disease
Chungwoo Shin, In-Cheol Baek, Won Kyoung Cho, Tai-Gyu Kim, Byung-Kyu Suh
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the status of treatment of benign thyroid diseases — a public health problem aggravated in the COVID-19 pandemic era
Giulianno Molina Melo, Antonio José Gonçalves, Fernando Walder, Carolina Ferraz, Murilo Catafesta Neves, Marcio Abrahão, Onivaldo Cervantes
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2022; 88(6): 982. CrossRef - Graves’ disease and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: a Korean population-based study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Jinyoung Youn, Ji Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Brain Communications.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Graves’ Disease and the Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Korean Population-Based Study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Hye Ryoun Jang, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 281. CrossRef - Incidence of hypothyroidism after treatment for breast cancer: A Korean population-based study
Jongmoo Park, Choongrak Kim, Yongkan Ki, Wontaek Kim, Jiho Nam, Donghyun Kim, Dahl Park, Hosang Jeon, Dong Woon Kim, Ji Hyeon Joo, Claudio Andaloro
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269893. CrossRef - Genome-wide association study of hyperthyroidism based on electronic medical record from Taiwan
Ting-Yuan Liu, Wen-Ling Liao, Tzu-Yuan Wang, Chia-Jung Chan, Jan-Gowth Chang, Yu-Chia Chen, Hsing-Fang Lu, Hsien-Hui Yang, Shih-Yin Chen, Fuu-Jen Tsai
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Graves’ disease, its treatments, and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A Korean population-based study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dughyun Choi, Chul-Hee Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Jee Soo Kim, Seung-Jung Park, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of autoimmune diseases in recurrent aphthous ulcer patients: A nationwide population study
Young Chan Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Young‐Gyu Eun, Ran Song, In‐Hwan Oh
Oral Diseases.2021; 27(6): 1443. CrossRef - Hyperthyroidism Prevalence in China After Universal Salt Iodization
Chuyuan Wang, Yongze Li, Di Teng, Xiaoguang Shi, Jianming Ba, Bing Chen, Jianling Du, Lanjie He, Xiaoyang Lai, Yanbo Li, Haiyi Chi, Eryuan Liao, Chao Liu, Libin Liu, Guijun Qin, Yingfen Qin, Huibiao Quan, Bingyin Shi, Hui Sun, Xulei Tang, Nanwei Tong, Gui
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comorbidity network analysis related to obesity in middle-aged and older adults: findings from Korean population-based survey data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021018. CrossRef - Prevalence of Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism and its Correlation with Serum Antithyroglobulin among patients in Kirkuk-Iraq
Sabah Mohammed Salih, Wijdan Abdullameer Kamel, Mohammed Talat Abbas, Kasim Sakran Abass
Journal Of Advanced Pharmacy Education And Research.2021; 11(2): 57. CrossRef - A nationwide study of patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance with a 10-year follow-up in South Korea
Ka-Won Kang, Ji Eun Song, Byung-Hyun Lee, Min Ji Jeon, Eun Sang Yu, Dae Sik Kim, Se Ryeon Lee, Hwa Jung Sung, Chul Won Choi, Yong Park, Byung Soo Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and Mortality of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke in Patients with Hyperthyroidism: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea
Hyun Jung Kim, Taeuk Kang, Min Ji Kang, Hyeong Sik Ahn, Seo Young Sohn
Thyroid.2020; 30(7): 955. CrossRef - Vitamin D supplementation does not prevent the recurrence of Graves’ disease
Yoon Young Cho, Yun Jae Chung
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Binding and Activity of Tetrabromobisphenol A Mono-Ether Structural Analogs to Thyroid Hormone Transport Proteins and Receptors
Xiao-Min Ren, Linlin Yao, Qiao Xue, Jianbo Shi, Qinghua Zhang, Pu Wang, Jianjie Fu, Aiqian Zhang, Guangbo Qu, Guibin Jiang
Environmental Health Perspectives.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome and its components in Chinese patients with a range of thyroid-stimulating hormone concentrations
Kun Tang, Qiao Zhang, Nian-chun Peng, Miao Zhang, Shu-jing Xu, Hong Li, Ying Hu, Chun-ju Xue, Li-xin Shi
Journal of International Medical Research.2020; 48(11): 030006052096687. CrossRef - The Association of Overt and Subclinical Hyperthyroidism with the Risk of Cardiovascular Events and Cardiovascular Mortality: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Cohort Studies
Seo Young Sohn, Eunyoung Lee, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 786. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Disease in Patients Surgically Treated for Pituitary Disease
Kim, Cho, Ku, Jung, Moon, Kim, Shin, Kim, Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(8): 1142. CrossRef - Association of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Hormones with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Euthyroid Children and Adolescents Aged 10–18 Years: A Population-Based Study
Cheol Gyu Ma, Young Suk Shim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight change is significantly associated with risk of thyroid cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Cheol-Young Park
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the relationship of subclinical hypothyroidism with metabolic syndrome and its components in adolescents: a population-based study
Min-Kyung Lee, Yoo Mee Kim, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Young Jun Won, Se Hwa Kim
Endocrine.2019; 65(3): 608. CrossRef - Autoimmune thyroiditis and central serous chorioretinopathy may have a relation
Brijesh Takkar, Harsha Saxena, Anubha Rathi, Rekha Singh
Medical Hypotheses.2018; 121: 180. CrossRef
- Diabetes
- Pioglitazone Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Inflammation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pancreatic β-Cells
-
Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):105-113. Published online March 21, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.105
-
-
6,244
View
-
96
Download
-
19
Web of Science
-
23
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activator gamma (PPARγ) is a useful therapeutic target for obesity and diabetes, but its role in protecting β-cell function and viability is unclear. MethodsTo identify the potential functions of PPARγ in β-cells, we treated mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells with the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone in conditions of lipotoxicity, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and inflammation. ResultsPalmitate-treated cells incubated with pioglitazone exhibited significant improvements in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and the repression of apoptosis, as shown by decreased caspase-3 cleavage and poly (adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose) polymerase activity. Pioglitazone also reversed the palmitate-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 6 [IL-6], and IL-1β) and ER stress markers (phosphor-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α, glucose-regulated protein 78 [GRP78], cleaved-activating transcription factor 6 [ATF6], and C/EBP homologous protein [CHOP]), and pioglitazone significantly attenuated inflammation and ER stress in lipopolysaccharide- or tunicamycin-treated MIN6 cells. The protective effect of pioglitazone was also tested in pancreatic islets from high-fat-fed KK-Ay mice administered 0.02% (wt/wt) pioglitazone or vehicle for 6 weeks. Pioglitazone remarkably reduced the expression of ATF6α, GRP78, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, prevented α-cell infiltration into the pancreatic islets, and upregulated glucose transporter 2 (Glut2) expression in β-cells. Moreover, the preservation of β-cells by pioglitazone was accompanied by a significant reduction of blood glucose levels. ConclusionAltogether, these results support the proposal that PPARγ agonists not only suppress insulin resistance, but also prevent β-cell impairment via protection against ER stress and inflammation. The activation of PPARγ might be a new therapeutic approach for improving β-cell survival and insulin secretion in patients with diabetes mellitus
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nr1h4 and Thrb ameliorate ER stress and provide protection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s
Nancy Ahuja, Shalini Gupta, Rashmi Arora, Ella Bhagyaraj, Drishti Tiwari, Sumit Kumar, Pawan Gupta
Life Science Alliance.2024; 7(7): e202302416. CrossRef - Prosthetic vascular grafts engineered to combat calcification: Progress and future directions
Taylor K. Brown, Sara Alharbi, Karen J. Ho, Bin Jiang
Biotechnology and Bioengineering.2023; 120(4): 953. CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes mellitus, and cardiometabolic risk: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2023
Harold Edward Bays, Shagun Bindlish, Tiffany Lowe Clayton
Obesity Pillars.2023; 5: 100056. CrossRef - Metformin promotes osteogenic differentiation and prevents hyperglycaemia-induced osteoporosis by suppressing PPARγ expression
Lifeng Zheng, Ximei Shen, Yun Xie, Hong Lian, Sunjie Yan, Shizhong Wang
Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.2023; 55(3): 394. CrossRef - Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors as targets to treat metabolic diseases: Focus on the adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas
Henrique Souza-Tavares, Carolline Santos Miranda, Isabela Macedo Lopes Vasques-Monteiro, Cristian Sandoval, Daiana Araujo Santana-Oliveira, Flavia Maria Silva-Veiga, Aline Fernandes-da-Silva, Vanessa Souza-Mello
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 29(26): 4136. CrossRef - Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase upregulation contributes to palmitate-elicited peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor transactivation in hepatocytes
Qing Song, Jun Wang, Alexandra Griffiths, Samuel Man Lee, Iredia D. Iyamu, Rong Huang, Jose Cordoba-Chacon, Zhenyuan Song
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2023; 325(1): C29. CrossRef - The global perspective on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in ectopic fat deposition: A review
Yanhao Qiu, Mailin Gan, Xingyu Wang, Tianci Liao, Qiuyang Chen, Yuhang Lei, Lei Chen, Jinyong Wang, Ye Zhao, Lili Niu, Yan Wang, Shunhua Zhang, Li Zhu, Linyuan Shen
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 253: 127042. CrossRef - Chemical inducer of regucalcin attenuates lipopolysaccharide‐induced inflammatory responses in pancreatic MIN6 β‐cells and RAW264.7 macrophages
Tomiyasu Murata, Kazunori Hashimoto, Susumu Kohno, Chiaki Takahashi, Masayoshi Yamaguchi, Chihiro Ito, Itoigawa Masataka, Roji Kojima, Kiyomi Hikita, Norio Kaneda
FEBS Open Bio.2022; 12(1): 175. CrossRef - Targets for rescue from fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells
Seok-Woo Hong, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 57. CrossRef - Analysis of changes in the proteomic profile of porcine corpus luteum during different stages of the oestrous cycle: effects of PPAR gamma ligands
Zuzanna Kunicka, Karol Mierzejewski, Aleksandra Kurzyńska, Robert Stryiński, Jesús Mateos, Mónica Carrera, Monika Golubska, Iwona Bogacka, Xiaolong Wang
Reproduction, Fertility and Development.2022; 34(11): 776. CrossRef - Activation of PPARγ Protects Obese Mice from Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Yin Tang, Ke Wei, Ling Liu, Jingyue Ma, Siqi Wu, Wenjing Tang, Stéphane Mandard
PPAR Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Pioglitazone on endoplasmic reticulum stress regarding in situ perfusion rat model
Vivien Telek, Luca Erlitz, Ibitamuno Caleb, Tibor Nagy, Mónika Vecsernyés, Bálint Balogh, György Sétáló, Péter Hardi, Gábor Jancsó, Ildikó Takács
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2021; 79(2): 311. CrossRef - Inflammation in Metabolic Diseases and Insulin Resistance
Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(2): 31. CrossRef - Current Status of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Type II Diabetes
Sagir Mustapha, Mustapha Mohammed, Ahmad Khusairi Azemi, Abubakar Ibrahim Jatau, Aishatu Shehu, Lukman Mustapha, Ibrahim Muazzamu Aliyu, Rabi’u Nuhu Danraka, Abdulbasit Amin, Auwal Adam Bala, Wan Amir Nizam Wan Ahmad, Aida Hanum Ghulam Rasool, Mohd Rais M
Molecules.2021; 26(14): 4362. CrossRef - JunD Regulates Pancreatic β-Cells Function by Altering Lipid Accumulation
Kexin Wang, Yixin Cui, Peng Lin, Zhina Yao, Yu Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pioglitazone even at low dosage improves NAFLD in type 2 diabetes: clinical and pathophysiological insights from a subgroup of the TOSCA.IT randomised trial
Giuseppe Della Pepa, Marco Russo, Marilena Vitale, Fabrizia Carli, Claudia Vetrani, Maria Masulli, Gabriele Riccardi, Olga Vaccaro, Amalia Gastaldelli, Angela A. Rivellese, Lutgarda Bozzetto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108984. CrossRef - Radioprotective Effect of Pioglitazone Against Genotoxicity Induced by Ionizing Radiation in Healthy Human Lymphocytes
Roya Kazemi, Seyed J. Hosseinimehr
Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry .2021; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Recent Insights Into Mechanisms of β-Cell Lipo- and Glucolipotoxicity in Type 2 Diabetes
Maria Lytrivi, Anne-Laure Castell, Vincent Poitout, Miriam Cnop
Journal of Molecular Biology.2020; 432(5): 1514. CrossRef - Artemisinin and dihydroartemisinin promote β-cell apoptosis induced by palmitate via enhancing ER stress
Ke Chen, Hu Hua, Ziyang Zhu, Tong Wu, Zhanjun Jia, Qianqi Liu
Apoptosis.2020; 25(3-4): 192. CrossRef - Mechanisms of impaired pancreatic β‑cell function in high‑fat diet‑induced obese mice: The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress
Xiaoqing Yi, Xuan Cai, Sisi Wang, Yanfeng Xiao
Molecular Medicine Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids Prevent Altered-Muc2 Secretion Induced by Palmitic Acid by Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in LS174T Goblet Cells
Quentin Escoula, Sandrine Bellenger, Michel Narce, Jérôme Bellenger
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2179. CrossRef - PPAR-γ agonist, pioglitazone, reduced oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with L-NAME-induced hypertension in rats
Eman Soliman, Shereen F. Behairy, Nabila N. El-maraghy, Shimaa M. Elshazly
Life Sciences.2019; 239: 117047. CrossRef - Changes of MODY signal pathway genes in the endoplasmic reticulum stress in INS-1-3 cells
Yanan Dong, Shirui Li, Wenhui Zhao, Yanlei Wang, Tingting Ge, Jianzhong Xiao, Yukun Li, Herve Le Stunff
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0198614. CrossRef
- Diabetes
- The Association between Persistent Hypertriglyceridemia and the Risk of Diabetes Development: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
-
Yu Hyun Kwon, Seul-Ki Kim, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):55-61. Published online January 30, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.55
-
-
4,167
View
-
62
Download
-
13
Web of Science
-
14
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Hypertriglyceridemia is known to have an association with increased risks of insulin resistance and diabetes. The aim of this study was to investigate the risk of diabetes mellitus, according to changes in the concentrations of triglycerides, over time. MethodsA total of 15,932 non-diabetic participants (mean age 43.2 years, 68% men) who attended five consecutive annual health check-ups at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, between January 2010 and December 2014, were recruited. Participants were classified according to their triglyceride concentrations; normal (<150 mg/dL) and abnormal (≥150 mg/dL). According to the triglyceride levels in 2010 and 2012, subjects were divided into four groups: normal-normal, normal-abnormal, abnormal-normal, and abnormal-abnormal. The risk for incident diabetes was assessed in 2014. ResultsAmong the total subjects, 67.5% belonged to the normal-normal group, 8.6% to the normal-abnormal group, 9.4% to the abnormal-normal group, and 14.5% to the abnormal-abnormal group. A total of 234 subjects (1.5%) were newly diagnosed with diabetes, between 2010 and 2014. Over 4 years, 1%, 1.5%, 2.1%, and 3.0% of the subjects developed diabetes in the normal-normal, normal-abnormal, abnormal-normal, and abnormal-abnormal groups, respectively. When the risk for incident diabetes was analyzed in the groups, after adjusting the confounding variables, a 1.58-fold increase in the risk of diabetes (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 2.26) was observed in the participants with persistent hypertriglyceridemia (abnormal-abnormal group). This was attenuated by further adjustments for body mass index (BMI) (hazard ratio, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.80). ConclusionIn this large study population, persistent hypertriglyceridemia, over a period of 2 years, was significantly associated with the risk of incident diabetes, which was attenuated after adjustment for BMI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jong-Dai Kim, Moon Jung Kim, Byungpyo Kim, Jung Heo, Jiyeon Ahn, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111109. CrossRef - Usefulness of SPISE Index for Screening and Detection of Early Stages of Insulin Resistance among Chilean Young Adults
Isabel Pereyra González, Sandra Lopez-Arana
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2023; 79(4): 372. CrossRef - Lipid variability in patients with diabetes mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(4): 126. CrossRef - Sesamin: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Ameliorating Symptoms of Diabetes
Shu-Ming Huang, Cheng-Hung Chuang, Christine Joyce F. Rejano, Lemmuel L. Tayo, Cheng-Yang Hsieh, Steven Kuan-Hua Huang, Po-Wei Tsai
Molecules.2023; 28(21): 7255. CrossRef - Variability, Mean, and Baseline Values of Metabolic Parameters in Predicting Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Duong Duc Pham, Jaekyung Song, Yunwan Jeon, Ibrahimi Hajar, Chae Hun Leem
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(5): 1270. CrossRef - Lipid Variability and Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 28. CrossRef - The Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Russian Population Cohort According to Data from the HAPIEE Project
Svetlana V. Mustafina, Oksana D. Rymar, Liliya V. Shcherbakova, Evgeniy G. Verevkin, Hynek Pikhart, Olga V. Sazonova, Yuliya I. Ragino, Galina I. Simonova, Martin Bobak, Sofia K. Malyutina, Mikhail I. Voevoda
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(2): 119. CrossRef - The influence of VDR polymorphisms on the type 2 diabetes susceptibility in Chinese: an interaction with hypertriglyceridemia
Dongdong Zhang, Cheng Cheng, Yan Wang, Yuan Xue, Yaping Liu, Yiming Liu, Mingming Feng, Ze Xu, Wenjie Li, Xing Li
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2021; 296(4): 837. CrossRef - Development and validation of a new diabetes index for the risk classification of present and new-onset diabetes: multicohort study
Shinje Moon, Ji-Yong Jang, Yumin Kim, Chang-Myung Oh
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia as an Independent Predictor for Ten-Year Incidence of Diabetes in Thais
Suranut Charoensri, Supatida Turnsaket, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
Vascular Health and Risk Management.2021; Volume 17: 519. CrossRef - Prevalence and Current Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 85. CrossRef - HDL-Cholesterol, Its Variability, and the Risk of Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Seung-Hwan Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(11): 5633. CrossRef - Response: The Association between Persistent Hypertriglyceridemia and the Risk of Diabetes Development: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study (Endocrinol Metab 2018;33:55–61, Yu Hyun Kwon et al.)
Eun-Jung Rhee, Yu Hyun Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(3): 425. CrossRef - The Association between Persistent Hypertriglyceridemia and the Risk of Diabetes Development: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study (Endocrinol Metab 2018;33:55–61, Yu Hyun Kwon et al.)
Mi Hae Seo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 305. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Changes in Body Composition According to Age and Sex among Young Non-Diabetic Korean Adults: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
-
Seul-Ki Kim, Yu-Hyun Kwon, Jung Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(4):442-450. Published online November 21, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.4.442
-
-
6,175
View
-
63
Download
-
18
Web of Science
-
20
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Age-related decreases in lean mass represent a serious health problem. We aimed to analyze the risks of rapid decreases in lean mass by age and sex in relatively young Korean adults during a 4-year follow-up study. MethodsA total of 65,856 non-diabetic participants (59.5% men, mean age 39.1 years) in a health screening program were subjected to bioimpedance body composition analyses and metabolic parameter analyses at baseline and after 4 years. The participants were sub-divided according to age, and additionally to six groups by age and the degree of body weight change over the 4-year period. The actual changes in body weight, lean mass, and fat mass and the percent changes over the 4-year period were assessed. ResultsThe percent change in lean mass decreased and the percent change of fat mass increased with increasing age in every age and sex group. However, the annual percent decrease in lean mass and percent increase in fat mass were significantly higher among women than among men (−0.26% vs. −0.15% and 0.34% vs. 0.42%, respectively; P<0.01). Participants who were older than 50 years and had a weight loss <−5% during the 4 years had significantly greater decreases in lean mass and smaller decreases in fat mass, compared to those who were younger than 50 years. An odds ratio analysis to determine the lowest quartile of the percent change in lean mass according to age group revealed that participants older than 60 years had a significantly increased risk of a rapid decrease in the lean mass percentage (2.081; 95% confidence interval, 1.678 to 2.581). ConclusionEven in this relatively young study population, the lean mass decreased significantly with age, and the risk of a rapid decrease in lean mass was higher among women than among men. Furthermore, the elderly exhibited a significantly more rapid decrease in lean mass, compared with younger participants.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Obesity, Physical Performance, Balance Confidence, and Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results from the Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study
Ga Yang Shim, Myung Chul Yoo, Yunsoo Soh, Jinmann Chon, Chang Won Won
Nutrients.2024; 16(5): 614. CrossRef - Multisystem physiological perspective of human frailty and its modulation by physical activity
Joseph A. Taylor, Paul L. Greenhaff, David B. Bartlett, Thomas A. Jackson, Niharika A. Duggal, Janet M. Lord
Physiological Reviews.2023; 103(2): 1137. CrossRef - Partial weight reduction protocols in cats lead to better weight outcomes, compared with complete protocols, in cats with obesity
Alexander J. German, Georgiana R. T. Woods-Lee, Vincent Biourge, John Flanagan
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multifaceted effects of obesity on cancer immunotherapies: Bridging preclinical models and clinical data
Logan V. Vick, Robert J. Canter, Arta M. Monjazeb, William J. Murphy
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2023; 95: 88. CrossRef - Age-Related Trends in Body Composition among Women Aged 20–80 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nirmala Rathnayake, Hasanga Rathnayake, Sarath Lekamwasam, Aron Weller
Journal of Obesity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Increased Consumption of Unsaturated Fatty Acids Improves Body Composition in a Hypercholesterolemic Chinese Population
Sumanto Haldar, Shalini Ponnalagu, Farhana Osman, Shia Lyn Tay, Long Hui Wong, Yuan Rong Jiang, Melvin Khee Shing Leow, Christiani Jeyakumar Henry
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Low-cost Dairy Food Supplement with Mauritia Flexuosa (Buriti) to Combat Malnutrition: Translational Study in Mice and Institutionalized Elderly Woman
Audrey Handyara Bicalho, Fabio Ribeiro Santos, Daniele Cristina Moreira, Victor Hugo Dantas Guimarães, Guilherme Henrique Ribeiro, Alfredo Mauricio Batista De Paula, André Luis Sena Guimarães, Ulisses A. Pereira, Theles Costa, Caroline Liboreiro Paiva, Ma
Current Aging Science.2022; 15(1): 37. CrossRef - The missense variant, rs373863828, in CREBRF plays a role in longitudinal changes in body mass index in Samoans
Haoyi Fu, Nicola L. Hawley, Jenna C. Carlson, Emily M. Russell, Alysa Pomer, Hong Cheng, Take Naseri, Muagututi‘a Sefuiva Reupena, Ranjan Deka, Courtney C. Choy, Stephen T. McGarvey, Ryan L. Minster, Daniel E. Weeks
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2022; 16(3): 220. CrossRef - Relationship Between Handgrip Strength and the Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Among Korean Adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2014-2018
Sung-hyun Hong, Ji-yong Byeon, Ji-hee Min, Dong-hyuk Park, Won-hee Cho, Justin Y. Jeon
Exercise Science.2021; 30(1): 110. CrossRef - Cutoff points of adiposity anthropometric indices for low muscle mass screening in middle-aged and older healthy women
Rafaela Andrade do Nascimento, Mariana Carmem Apolinário Vieira, Rafaella Silva dos Santos Aguiar Gonçalves, Mayle Andrade Moreira, Maria Socorro Medeiros de Morais, Saionara Maria Aires da Câmara, Álvaro Campos Cavalcanti Maciel
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Edema-like symptoms are common in ultra-distance cyclists and driven by overdrinking, use of analgesics and female sex – a study of 919 athletes
Philipp Gauckler, Jana S. Kesenheimer, Andreas Kronbichler, Fiona R. Kolbinger
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of low muscle mass and associated factors in community-dwelling older adults in Singapore
Siew Ling Tey, Dieu Thi Thu Huynh, Yatin Berde, Geraldine Baggs, Choon How How, Yen Ling Low, Magdalin Cheong, Wai Leng Chow, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Samuel Teong Huang Chew
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of low skeletal muscle mass and sarcopenic obesity on albuminuria: a 7-year longitudinal study
Jee Hee Yoo, Gyuri Kim, Sung Woon Park, Min Sun Choi, Jiyeon Ahn, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Age group and gender-wise comparison of obesity indices in subjects of Varanasi
Kumar Sarvottam, Prabhat Ranjan, Umashree Yadav
Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2020; 64: 109. CrossRef - DNA Methylation in Inflammatory Pathways Modifies the Association between BMI and Adult-Onset Non-Atopic Asthma
Ayoung Jeong, Medea Imboden, Akram Ghantous, Alexei Novoloaca, Anne-Elie Carsin, Manolis Kogevinas, Christian Schindler, Gianfranco Lovison, Zdenko Herceg, Cyrille Cuenin, Roel Vermeulen, Deborah Jarvis, André Amaral, Florian Kronenberg, Paolo Vineis, Nic
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(4): 600. CrossRef - Body shape, fear of falling, physical performance, and falls among individuals aged 55 years and above
Sheng Hui Kioh, Sumaiyah Mat, Shahrul B. Kamaruzzaman, Fatimah Ibrahim, Mas Sahidayana Mokhtar, Noran N. Hairi, Robert G. Cumming, Phyo Kyaw Myint, Maw Pin Tan
European Geriatric Medicine.2019; 10(5): 801. CrossRef - Low lean tissue mass can be a predictor of one-year survival in hemodialysis patients
Aleksandra Rymarz, Julia Gibińska, Maria Zajbt, Wiesław Piechota, Stanisław Niemczyk
Renal Failure.2018; 40(1): 231. CrossRef - Relationship Between Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 7‐Year Longitudinal Study
Gyuri Kim, Seung‐Eun Lee, You‐Bin Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon‐Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Hepatology.2018; 68(5): 1755. CrossRef - Association between abdominal obesity and increased risk for the development of hypertension regardless of physical activity: A nationwide population‐based study
Eun‐Jung Rhee, Jung‐Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se‐Eun Park, Jin‐Hyung Jung, Kyung‐Do Han, Yong‐Gyu Park, Hye Soon Park, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Soon‐Jib Yoo, Won‐Young Lee
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2018; 20(10): 1417. CrossRef - Decreasing Lean Body Mass with Age: Challenges and Opportunities for Novel Therapies
Chrysoula Boutari, Christos S. Mantzoros
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(4): 422. CrossRef
- Endocrinology and Metabolism Is Indexed in the Emerging Sources Citation Index
-
Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(3):350-352. Published online September 18, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.3.350
-
-
4,289
View
-
44
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Triennial Report ofEndocrinology and Metabolism, 2015 to 2017
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hey Yeon Jang, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 195. CrossRef
- New Potential Targets of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Pancreatic β-Cells and Hepatocytes
-
Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):1-5. Published online February 6, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.1
-
-
4,192
View
-
43
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
It is well known that both insulin resistance and decreased insulin secretory capacity are important factors in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In addition to genetic factors, obesity and lipotoxicity can increase the risk of T2DM. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are novel antidiabetic drugs with multiple effects. They can stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit postprandial glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and induce pancreatic β-cell proliferation. They can also reduce the weight of patients with T2DM and relieve lipotoxicity at the cellular level. Many intracellular targets of GLP-1 have been found, but more remain to be identified. Elucidating these targets could be a basis for developing new potential drugs. My colleagues and I have investigated new targets of GLP-1, with a particular focus on pancreatic β-cell lines and hepatic cell lines. Herein, I summarize the recent work from my laboratory, with profound gratitude for receiving the prestigious 2016 Namgok Award. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Venom Peptides, Polyphenols and Alkaloids: Are They the Next Antidiabetics That Will Preserve β-Cell Mass and Function in Type 2 Diabetes?
Michele Lodato, Valérie Plaisance, Valérie Pawlowski, Maxime Kwapich, Alexandre Barras, Emeline Buissart, Stéphane Dalle, Sabine Szunerits, Jérôme Vicogne, Rabah Boukherroub, Amar Abderrahmani
Cells.2023; 12(6): 940. CrossRef - Diabetes, Incretin Therapy and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm – What Does the Evidence Show?
Camilla Krizhanovskii , Anders Franco-Cereceda
Current Vascular Pharmacology.2019; 17(5): 432. CrossRef - Toll-like receptor 4 is necessary for glucose-dependent glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in male mice
Lijuan Wang, Xiandong Zhan, Zhenhui Wang, Jing Ma, Xiaotong Chang, Xiaobo Zhu
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2019; 510(1): 104. CrossRef
- Articles in Endocrinology and Metabolism in 2016
-
Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):62-67. Published online March 20, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.62
-
-
3,503
View
-
40
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Insulin Resistance and Glucose Metabolism during Infection
Borros Arneth
Endocrines.2023; 4(4): 685. CrossRef - Effects of 6 Months of Dapagliflozin Treatment on Metabolic Profile and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction for Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients without Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Ju-Young Hong, Keun-Young Park, Jong-Dai Kim, Won-Min Hwang, Dong-Mee Lim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2020; 29(3): 215. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Waist Circumference as a Marker of Obesity Is More Predictive of Coronary Artery Calcification than Body Mass Index in Apparently Healthy Korean Adults: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
-
Jongsin Park, Eun Seo Lee, Da Young Lee, Jihyun Kim, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):559-566. Published online December 20, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.559
-
-
4,553
View
-
38
Download
-
33
Web of Science
-
30
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
We aimed to assess the risk for coronary artery calcification (CAC) according to groups subdivided by body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) in apparently healthy Korean adults. MethodsThirty-three thousand four hundred and thirty-two participants (mean age, 42 years) in a health screening program were divided into three groups according to BMI: <23 kg/m2 (normal), 23 to 25 kg/m2 (overweight), and >25 kg/m2 (obese). In addition, the participants were divided into two groups according to WC. Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) was measured with multi-detector computed tomography in all participants. Presence of CAC was defined as CACS >0. ResultsWhen logistic regression analysis was performed with the presence of CAC as the dependent variable, the risk for CAC increased as BMI increased after adjusting for confounding variables (1.102 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.000 to 1.216]; 1.284 [95% CI, 1.169 to 1.410]; in the overweight and obese groups vs. the normal weight group). When the participants were divided into six groups according to BMI and WC, the subjects with BMI and WC in the obese range showed the highest risk for CAC (1.321 [95% CI, 1.194 to 1.461]) and those with BMI in the overweight range and WC in the obese range showed the second highest risk for CAC (1.235 [95% CI, 1.194 to 1.461]). ConclusionParticipants with obesity defined by both BMI and WC showed the highest risk for CAC. Those with BMIs in the overweight range but with WC in the obese range showed the second highest risk for CAC, suggesting that WC as a marker of obesity is more predictive of CAC than BMI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Insulin Secretory Capacity and Insulin Resistance in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
-
Jong-Dai Kim, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):354-360. Published online August 16, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.354
-
-
4,463
View
-
42
Download
-
16
Web of Science
-
16
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
It is well known that many Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were non-obese and had decreased insulin secretion in past. However, during the past three decades, lifestyles in Korea have been westernized. As a result, the prevalence of obesity, the main cause of diabetes has increased. Thus, there is still a question as to whether the main pathophysiology of current Korean T2DM is insulin resistance or an insulin secretion defect. Because various anti-diabetes medications having different mechanisms of action are currently used as therapeutics, it is important to understand which of these factors is the main physiology in the development of diabetes in Koreans. In this review, we review changes in obesity prevalence, insulin resistance and insulin secretion defects in Korean T2DM during three decades. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Association of polygenic risk scores for insulin resistance risk and their interaction with a plant-based diet, especially fruits, vitamin C, and flavonoid intake, in Asian adults
Sunmin Park
Nutrition.2023; 111: 112007. CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index Cutoff Point Is an Accurate Marker for Predicting the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Caucasian Subjects
David Primo, Olatz Izaola, Daniel A. de Luis
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2023; 79(2): 238. CrossRef - A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Waist circumference, body mass index, and colorectal cancer risk according to diabetes status: A Korean nationwide population‐based cohort study
Dae Bum Kim, Kang‐Moon Lee, Ji Min Lee, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Kyung‐Do Han, Yong Gyu Park
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(2): 397. CrossRef - Glucose‐lowering action through targeting islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: Focus on dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibition
Bo Ahrén
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(7): 1128. CrossRef - The triglyceride–glucose index is a more powerful surrogate marker for predicting the prevalence and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus than the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance
Hye Min Park, Hye Sun Lee, Yong-Jae Lee, Jun-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 180: 109042. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Pioglitazone versus Glimepiride after Metformin and Alogliptin Combination Therapy: A Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter, Parallel-Controlled Study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Ja Young Park, Eun Sook Kim, Kwang Jae Lee, Young Sik Choi, Duk Kyu Kim, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 67. CrossRef - Effect of roux-en Y gastric bypass surgery on patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ke-Yan Chen, Ying-Li Liu, Jin-Cai Shang, De-Wang Su, Rong-Rong Yao, De-Zhi Ke, Hao Tian
Medicine.2020; 99(23): e20382. CrossRef - Diabetes, microRNA, and Nutrition in Geriatrics
Telma Angelina Faraldo Corrêa, Marcelo Macedo Rogero
Current Geriatrics Reports.2020; 9(4): 229. CrossRef - High genetic risk scores of SLIT3, PLEKHA5 and PPP2R2C variants increased insulin resistance and interacted with coffee and caffeine consumption in middle-aged adults
J.W. Daily, M. Liu, S. Park
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2019; 29(1): 79. CrossRef - Failure of monotherapy in clinical practice in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Korean National Diabetes Program
Ja Young Jeon, Soo Jin Lee, Sieun Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan‐Woo Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(5): 1144. CrossRef - Efficacy and tolerability of novel triple combination therapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes from the TRIPLE-AXEL trial: protocol for an open-label randomised controlled trial
Nam Hoon Kim, Soo Lim, Soo Heon Kwak, Min Kyong Moon, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-ho Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Juneyoung Lee, Sin Gon Kim
BMJ Open.2018; 8(9): e022448. CrossRef - Impact of systemic inflammation on the relationship between insulin resistance and all-cause and cancer-related mortality
Da Young Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Yoosoo Chang, Chong Il Sohn, Ho-Cheol Shin, Seungho Ryu, Won-Young Lee
Metabolism.2018; 81: 52. CrossRef - Fimasartan increases glucose‐stimulated insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension compared with amlodipine
Ye Seul Yang, Min Hyuk Lim, Seong Ok Lee, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Soo Heon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Sungwan Kim, Andrea Mari, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(7): 1670. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance and Its Association with Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children
Jinkyung Cho, Haeryun Hong, Soohyun Park, Shinuk Kim, Hyunsik Kang
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Eligibility for Statin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Reduced Renal Function: An Observational Study
-
Byung Sub Moon, Jongho Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hyang Kim, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):402-409. Published online August 26, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.402
-
-
3,929
View
-
33
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between statin eligibility and the degree of renal dysfunction using the Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III and the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines in Korean adults. MethodsRenal function was assessed in 18,746 participants of the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study from January 2011 to December 2012. Subjects were divided into three groups according to estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR): stage 1, eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; stage 2, eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2; and stages 3 to 5, eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Statin eligibility in these groups was determined using the ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, and the risk for 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was calculated using the Framingham Risk Score (FRS) and Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE). ResultsThere were 3,546 (18.9%) and 4,048 (21.5%) statin-eligible subjects according to ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, respectively. The proportion of statin-eligible subjects increased as renal function deteriorated. Statin eligibility by the ACC/AHA guidelines showed better agreement with the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) recommendations compared to the ATP III guidelines in subjects with stage 3 to 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) (κ value, 0.689 vs. 0.531). When the 10-year ASCVD risk was assessed using the FRS and PCE, the mean risk calculated by both equations significantly increased as renal function declined. ConclusionsThe proportion of statin-eligible subjects significantly increased according to worsening renal function in this Korean cohort. ACC/AHA guideline showed better agreement for statin eligibility with that recommended by KDIGO guideline compared to ATP III in subjects with CKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Association between atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk and renal outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Honghong Ren, Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yiting Wang, Junlin Zhang, Yucheng Wu, Rui Zhang, Tingli Wang, Jiali Wang, Yitao Zhu, Ruikun Guo, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Mark E. Cooper, Fang Liu
Renal Failure.2021; 43(1): 477. CrossRef - Long-term effects of various types of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on changes in glomerular filtration rate in Korea
Seo Yeon Baik, Hyunah Kim, So Jung Yang, Tong Min Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Frontiers of Medicine.2019; 13(6): 713. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 274. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- C-Peptide-Based Index Is More Related to Incident Type 2 Diabetes in Non-Diabetic Subjects than Insulin-Based Index
-
Jong-Dai Kim, Sung Ju Kang, Min Kyung Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):320-327. Published online June 21, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.320
-
-
5,029
View
-
84
Download
-
45
Web of Science
-
45
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Diabetes can be efficiently prevented by life style modification and medical therapy. So, identification for high risk subjects for incident type 2 diabetes is important. The aim of this study is to identify the best β-cell function index to identify high risk subjects in non-diabetic Koreans. MethodsThis is a retrospective longitudinal study. Total 140 non-diabetic subjects who underwent standard 2-hour 75 g oral glucose tolerance test from January 2007 to February 2007 at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital and followed up for more than 1 year were analyzed (mean follow-up, 54.9±16.4 months). The subjects were consist of subjects with normal glucose tolerance (n=44) and subjects with prediabetes (n=97) who were 20 years of age or older. Samples for insulin and C-peptide levels were obtained at 0 and 30 minutes at baseline. ResultsThirty subjects out of 140 subjects (21.4%) developed type 2 diabetes. When insulin-based index and C-peptide-based index are compared between progressor and non-progressor to diabetes, all C-peptide-based indices were statistically different between two groups, but only insulinogenic index and disposition index among insulin-based index were statistically different. C-peptide-based index had higher value of area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AROC) value than that of insulin-based index. "C-peptidogenic" index had highest AROC value among indices (AROC, 0.850; 95% confidence interval, 0.761 to 0.915). C-peptidogenic index had significantly higher AROC than insulinogenic index (0.850 vs. 0.731 respectively; P=0.014). ConclusionC-peptide-based index was more closely related to incident type 2 diabetes in non-diabetic subjects than insulin-based index.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 
- Clinical Study
- Association of Waist-Height Ratio with Diabetes Risk: A 4-Year Longitudinal Retrospective Study
-
Yoon Jeong Son, Jihyun Kim, Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):127-133. Published online March 16, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.127
-
-
4,356
View
-
37
Download
-
26
Web of Science
-
24
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) is an easy and inexpensive adiposity index that reflects central obesity. In this study, we examined the association of various baseline adiposity indices, including WHtR, with the development of diabetes over 4 years of follow-up in apparently healthy Korean individuals. MethodsA total of 2,900 nondiabetic participants (mean age, 44.3 years; 2,078 men) in a health screening program, who repeated the medical check-up in 2005 and 2009, were recruited. Subjects were divided into two groups according to development of diabetes after 4 years. The cut-off values of baseline body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and WHtR for the development of diabetes over 4 years were calculated. The sensitivity, specificity, and mean area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUROC) of each index were assessed. The odds ratio (OR) for diabetes development was analyzed for each of the three baseline adiposity indices. ResultsDuring the follow-up period, 101 new cases (3.5%) of diabetes were diagnosed. The cut-off WHtR value for diabetes development was 0.51. Moreover, WHtR had the highest AUROC value for diabetes development among the three adiposity indices (0.716, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.669 to 0.763; 0.702, 95% CI, 0.655 to 0.750 for WC; 0.700, 95% CI, 0.651 to 0.750 for BMI). After adjusting for confounding variables, the ORs of WHtR and WC for diabetes development were 1.95 (95% CI, 1.14 to 3.34) and 1.96 (95% CI, 1.10 to 3.49), respectively. No significant differences were observed between the two groups regarding BMI. ConclusionIncreased baseline WHtR and WC correlated with the development of diabetes after 4 years. WHtR might be a useful screening measurement to identify individuals at high risk for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of waist circumference and waist‐to‐height ratio as predictors of clustering of cardiovascular risk factors among middle‐aged people in rural Khanh Hoa, Vietnam
Rachana Manandhar Shrestha, Thuy Thi Phuong Pham, Shohei Yamamoto, Chau Que Nguyen, Ami Fukunaga, Phan Cong Danh, Masahiko Hachiya, Huy Xuan Le, Hung Thai Do, Tetsuya Mizoue, Yosuke Inoue
American Journal of Human Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel anthropometric indices for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus
Erfan Sadeghi, Alireza Khodadadiyan, Seyed Ali Hosseini, Sayed Mohsen Hosseini, Ashraf Aminorroaya, Massoud Amini, Sara Javadi
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition and Cardiovascular Risk: A Study of Polish Military Flying Personnel
Agata Gaździńska, Stefan Gaździński, Paweł Jagielski, Paweł Kler
Metabolites.2023; 13(10): 1102. CrossRef - Cues of pregnancy decrease female physical attractiveness for males
Pavol Prokop, Martina Zvaríková, Milan Zvarík, Peter Fedor
Current Psychology.2022; 41(2): 697. CrossRef - Waist-to-height ratio has a stronger association with cardiovascular risks than waist circumference, waist-hip ratio and body mass index in type 2 diabetes
Jiang-Feng Ke, Jun-Wei Wang, Jun-Xi Lu, Zhi-Hui Zhang, Yun Liu, Lian-Xi Li
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 183: 109151. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of anthropometric indices for discriminating elevated blood pressure in pediatric population: a systematic review and a meta-analysis
Jun-Min Tao, Wei Wei, Xiao-Yang Ma, Ying-Xiang Huo, Meng-Die Hu, Xiao-Feng Li, Xin Chen
BMC Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The utilization of BMI in patients with high WHtR as to cardiovascular risk
Meliha Melin UYGUR
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(4): 1133. CrossRef - Assessment of obesity indices for prediction of hyperglycemia in adult population of Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh), India
Neha Rai, Hanjabam Barun Sharma, Renu Kumari, Jyotsna Kailashiya
Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2021; 64: 195. CrossRef - Waist-to-height ratio and metabolic phenotype compared to the Matsuda index for the prediction of insulin resistance
Katharina Lechner, Benjamin Lechner, Alexander Crispin, Peter E. H. Schwarz, Helene von Bibra
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Waist-to-Height Ratio (WHtR) in Predicting Coronary Artery Disease Compared to Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference in a Single Center from Saudi Arabia
Mostafa Q. Alshamiri, Faisal Mohd A Habbab, Saad Saeed AL-Qahtani, Khalil Abdullah Alghalayini, Omar Mohammed Al-Qattan, Fayez El-shaer, Anne Knowlton
Cardiology Research and Practice.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - A simple cut-off for waist-to-height ratio (0·5) can act as an indicator for cardiometabolic risk: recent data from adults in the Health Survey for England
Sigrid Gibson, Margaret Ashwell
British Journal of Nutrition.2020; 123(6): 681. CrossRef - Glucose Levels as a Mediator of the Detrimental Effect of Abdominal Obesity on Relative Handgrip Strength in Older Adults
Miguel Ángel Pérez-Sousa, Jesús del Pozo-Cruz, Carlos A. Cano-Gutiérrez, Atilio J. Ferrebuz, Carolina Sandoval-Cuellar, Mikel Izquierdo, Paula A. Hernández-Quiñonez, Robinson Ramírez-Vélez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(8): 2323. CrossRef Abnormal Glucose Metabolism and Associated Risk Factors Among Adults in Mekelle City, Ethiopia
Gebremedhin Gebreegziabiher, Tefera Belachew, Dessalegn Tamiru
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4017. CrossRefAnthropometric Indexes for Predicting High Blood Pressure in Vietnamese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study
Quan Nguyen Minh, Minh Hoang Nguyen Vo
Integrated Blood Pressure Control.2020; Volume 13: 181. CrossRef- Relation between Baseline Height and New Diabetes Development: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se-Eun Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 794. CrossRef - Issues in Measuring and Interpreting Diet and Its Contribution to Obesity
Rachael M. Taylor, Rebecca L. Haslam, Tracy L. Burrows, Kerith R. Duncanson, Lee M. Ashton, Megan E. Rollo, Vanessa A. Shrewsbury, Tracy L. Schumacher, Clare E. Collins
Current Obesity Reports.2019; 8(2): 53. CrossRef - Assessment of the validity of multiple obesity indices compared with obesity-related co-morbidities
Jaeeun Myung, Kyung Yoon Jung, Tae Hyun Kim, Euna Han
Public Health Nutrition.2019; : 1. CrossRef - Profiles of body mass index and blood pressure among young adults categorised by waist-to-height ratio cut-offs in Shandong, China
Ying-xiu Zhang, Shu-rong Wang
Annals of Human Biology.2019; 46(5): 409. CrossRef - Air Pollution Has a Significant Negative Impact on Intentional Efforts to Lose Weight: A Global Scale Analysis
Morena Ustulin, So Young Park, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Jeong-taek Woo, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 320. CrossRef - Being Metabolically Healthy, the Most Responsible Factor for Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Waist-to-height ratio index for predicting incidences of hypertension: the ARIRANG study
Jung Ran Choi, Sang Baek Koh, Eunhee Choi
BMC Public Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of various anthropometric indices for the identification of a predictor of incident hypertension: the ARIRANG study
J. R. Choi, S. V. Ahn, J. Y. Kim, S. B. Koh, E. H. Choi, G. Y. Lee, Y. E. Jang
Journal of Human Hypertension.2018; 32(4): 294. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - THE ASSESMENT OF RELATION BETWEEN WAIST/HEIGHT RATIO AND TYPE 2 DIABETES RISK AMONG NURSING STUDENTS
Ceren Gezer
Journal of Food and Health Science.2017; : 141. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- The Relationship between 10-Year Cardiovascular Risk Calculated Using the Pooled Cohort Equation and the Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
-
Jeong In Lee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Jihyun Kim, Eun Jin Han, Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):86-92. Published online March 16, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.86
-
-
4,755
View
-
40
Download
-
21
Web of Science
-
23
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
We investigated the association between the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the estimated 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) calculated by Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE) and Framingham risk score (FRS). MethodsA total of 15,913 participants (mean age, 46.3 years) in a health screening program were selected for analysis. The presence and severity of fatty liver was assessed by abdominal ultrasonogram. Subjects who drank alcohol more than three times a week were excluded from the study. ResultsAmong the participants, 57.6% had no NAFLD, 35.4% had grade I, 6.5% had grade II, and 0.5% had grade III NAFLD. Mean estimated 10-year CVD risk was 2.59%, 3.93%, 4.68%, and 5.23% calculated using the PCE (P for trend <0.01) and 4.55%, 6.39%, 7.33%, and 7.13% calculated using FRS, according to NAFLD severity from none to severe (P for trend <0.01). The odds ratio for ≥7.5% estimated CVD risk calculated using the PCE showed a higher correlation with increasing severity of NAFLD even after adjustment for conventional CVD risk factors (1.52, 2.56, 3.35 vs. the no NAFLD group as a reference, P<0.01) compared with calculated risk using FRS (1.65, 1.62, 1.72 vs. no NAFLD group as a reference, P<0.01). ConclusionIn our study of apparently healthy Korean adults, increasing severity of NAFLD showed a higher correlation with estimated 10-year CVD risk when calculated using the PCE than when calculated using FRS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Increases Cardiovascular Risk in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Dana Kablawi, Faisal Aljohani, Chiara Saroli Palumbo, Sophie Restellini, Alain Bitton, Gary Wild, Waqqas Afif, Peter L Lakatos, Talat Bessissow, Giada Sebastiani
Crohn's & Colitis 360.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Low Relative Handgrip Strength Is Associated with a High Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Italian Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Samantha Maurotti, Roberta Pujia, Elisa Mazza, Maria Francesca Pileggi, Franco Arturi, Maria Grazia Tarsitano, Tiziana Montalcini, Arturo Pujia, Yvelise Ferro
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(22): 12489. CrossRef - Fatty Liver Disease: Diagnosis and Stratification
Yedidya Saiman, Andres Duarte-Rojo, Mary E. Rinella
Annual Review of Medicine.2022; 73(1): 529. CrossRef - “Dangerous liaisons: NAFLD and liver fibrosis increase cardiovascular risk in HIV”
Adriana Cervo, Giada Sebastiani, Jovana Milic, Thomas Krahn, Sergio Mazzola, Salvatore Petta, Antonio Cascio, Giovanni Guaraldi, Giovanni Mazzola
HIV Medicine.2022; 23(8): 911. CrossRef - Value of the triglyceride glucose index combined with body mass index in identifying non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Nong Li, Huiwen Tan, Aixia Xie, Cheng Li, Xuan Fu, Weiting Xang, Amina Kirim, Xuefang Huang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relation Between Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease
Seyed Moayed Alavian, Hosein Zadi
Multidisciplinary Cardiovascular Annals.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for cardiovascular disease among individuals with hepatic steatosis
Julia Karády, Maros Ferencik, Thomas Mayrhofer, Nandini M. Meyersohn, Daniel O. Bittner, Pedro V. Staziaki, Balint Szilveszter, Travis R. Hallett, Michael T. Lu, Stefan B. Puchner, Tracey G. Simon, Borek Foldyna, Geoffrey S. Ginsburg, Robert W. McGarrah,
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(12): 3406. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index and Related Parameters (Triglyceride Glucose-Body Mass Index and Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference) Identify Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Overweight/Obesity
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Rowshanak Abbasi, Hoda Taheri, Maryam Lahouti, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(3): 167. CrossRef - Interplay between non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk in an asymptomatic general population
Grazia Pennisi, Vito Di Marco, Carola Buscemi, Giovanni Mazzola, Cristiana Randazzo, Federica Spatola, Antonio Craxì, Silvio Buscemi, Salvatore Petta
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(9): 2389. CrossRef - Non-Laboratory-Based Simple Screening Model for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Developed Using Multi-Center Cohorts
Jiwon Kim, Minyoung Lee, Soo Yeon Kim, Ji-Hye Kim, Ji Sun Nam, Sung Wan Chun, Se Eun Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Joo Young Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 823. CrossRef - Coronary Artery Disease is More Severe in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis than Fatty Liver
Toshihiro Niikura, Kento Imajo, Anna Ozaki, Takashi Kobayashi, Michihiro Iwaki, Yasushi Honda, Takaomi Kessoku, Yuji Ogawa, Masato Yoneda, Hiroyuki Kirikoshi, Satoru Saito, Atsushi Nakajima
Diagnostics.2020; 10(3): 129. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Disease in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Screening and Management
Hersh Shroff, Lisa B. VanWagner
Current Hepatology Reports.2020; 19(3): 315. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index Is Superior to the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance for Predicting Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults
Sang Bae Lee, Min Kyung Kim, Shinae Kang, Kahui Park, Jung Hye Kim, Su Jung Baik, Ji Sun Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Jong Suk Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(2): 179. CrossRef - Mortality Risk Detected by Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Score in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Pegah Golabi, Natsu Fukui, James Paik, Mehmet Sayiner, Alita Mishra, Zobair M. Younossi
Hepatology Communications.2019; 3(8): 1050. CrossRef - Lower hand grip strength in older adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a nationwide population-based study
Beom-Jun Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, Seung Hun Lee, Seongbin Hong, Mark W. Hamrick, Carlos M. Isales, Jung-Min Koh
Aging.2019; 11(13): 4547. CrossRef - Implication of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Metabolic Syndrome, and Subclinical Inflammation on Mild Renal Insufficiency
Ga Eun Nam, Soon Young Hwang, Hye Soo Chung, Ju Hee Choi, Hyun Jung Lee, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Implication of liver enzymes on incident cardiovascular diseases and mortality: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyung Mook Choi, Kyungdo Han, Sanghyun Park, Hye Soo Chung, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Seon Mee Kim
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Controlled Attenuation Parameter as a Noninvasive Method to Detect and Quantify Hepatic Steatosis in Chronic Liver Disease: What Is the Clinical Relevance
Mariana Verdelho Machado
GE - Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 24(4): 157. CrossRef - Effect of statin on hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide nested case‐control study
Gyuri Kim, Suk‐Yong Jang, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Se‐young Park, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
International Journal of Cancer.2017; 140(4): 798. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Increased risk for development of coronary artery calcification in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and systemic inflammation
Jihyun Kim, Da Young Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Susanne Kaser
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0180118. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Emerging Burden in Cardiometabolic and Renal Diseases
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 430. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Metabolic Health Is More Important than Obesity in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
-
Min-Kyung Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Jeong In Lee, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):522-530. Published online December 31, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.522
-
-
4,476
View
-
61
Download
-
23
Web of Science
-
23
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
The aim of this study is to compare the risk for future development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) according to different status of metabolic health and obesity. MethodsA total of 3,045 subjects without NAFLD and diabetes at baseline were followed for 4 years. Subjects were categorized into four groups according to the following baseline metabolic health and obesity statuses: metabolically healthy, non-obese (MHNO); metabolically healthy, obese (MHO); metabolically unhealthy, non-obese (MUHNO); and metabolically unhealthy, obese (MUHO). Being metabolically healthy was defined as having fewer than two of the following five components: high blood pressure, high fasting blood glucose, high triglyceride, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and being in the highest decile of the homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance index. Obesity was defined as a body mass index >25 kg/m2. The presence of NAFLD was assessed by ultrasonography. ResultsThe proportions of subjects included in the MHNO, MHO, MUHNO, and MUHO groups were 71.4%, 9.8%, 13.0%, and 5.8%, respectively. The proportions of subjects who developed NAFLD were 10.5%, 31.4%, 23.2%, and 42% in the MHNO, MHO, MUHNO, and MUHO groups, respectively. The risk for developing NAFLD was highest in subjects who were metabolically unhealthy both at baseline and after 4 years compared with subjects who were consistently metabolically healthy during the follow-up period (odds ratio, 2.862). Using the MHNO group as reference, the odds ratios for the MHO, MUHNO, and MUHO groups were 1.731, 1.877, and 2.501, respectively. ConclusionThe risk for NAFLD was lower in MHO subjects than in MUNO subjects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Increased metabolic variability in Korean patients with new onset bipolar disorder: a nationwide cohort study
Ji Hyun Baek, Kyungdo Han, Hyewon Kim, Kyojin Yang, Hong Jin Jeon
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased risk of incident atrial fibrillation in young adults with mental disorders: A nationwide population-based study
Hyun Jin Ahn, So-Ryoung Lee, Eue-Keun Choi, Nan Young Bae, Hyo-Jeong Ahn, Soonil Kwon, Seung-Woo Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Seil Oh, Gregory Y.H. Lip
Heart Rhythm.2023; 20(3): 365. CrossRef - Association between Sarcopenic Obesity Status and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Fibrosis
Wolhwa Song, Sung Hwan Yoo, Jinsun Jang, Su Jung Baik, Byoung Kwon Lee, Hyun Woong Lee, Jong Suk Park
Gut and Liver.2023; 17(1): 130. CrossRef - The impact of metabolic health on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). A single center experience
Anna Boulouta, Ioanna Aggeletopoulou, Stavros Kanaloupitis, Efthymios P Tsounis, Vasileios Issaris, Konstantinos Papantoniou, Anastasios Apostolos, Paraskevas Tsaplaris, Ploutarchos Pastras, Christos Sotiropoulos, Aggeliki Tsintoni, Georgia Diamantopoulou
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2022; 46(5): 101896. CrossRef - Lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Lean-NAFLD) and the development of metabolic syndrome: a retrospective study
Wenting Wang, Jianping Ren, Wenzhao Zhou, Jinyu Huang, Guomin Wu, Fenfang Yang, Shuang Yuan, Juan Fang, Jing Liu, Yao Jin, Haiyang Qi, Yuyang Miao, Yanna Le, Cenhong Ge, Xiantao Qiu, JinJing Wang, Ping Huang, Zixin Liu, Sheng Wang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease severity independent of visceral fat
Tsung‐Po Chen, Wen‐Yuan Lin, Chien‐Hsieh Chiang, Ting‐Hsin Shen, Kuo‐Chin Huang, Kuen‐Cheh Yang
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(10): 2903. CrossRef - Increased metabolic variability is associated with newly diagnosed depression: A nationwide cohort study
Ji Hyun Baek, Dong Wook Shin, Maurizio Fava, David Mischoulon, Hyewon Kim, Mi Jin Park, Eun Ji Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Hong Jin Jeon
Journal of Affective Disorders.2021; 294: 786. CrossRef - The expression signatures in liver and adipose tissue from obese Göttingen Minipigs reveal a predisposition for healthy fat accumulation
Susanna Cirera, Emirhan Taşöz, Mette Juul Jacobsen, Camilla Schumacher-Petersen, Berit Østergaard Christoffersen, Rikke Kaae Kirk, Trine Pagh Ludvigsen, Henning Hvid, Henrik Duelund Pedersen, Lisbeth Høier Olsen, Merete Fredholm
Nutrition & Diabetes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of obesity and metabolic health status in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A United Kingdom population-based cohort study using the health improvement network (THIN)
A. Vusirikala, T. Thomas, N. Bhala, A. A. Tahrani, G. N. Thomas, K. Nirantharakumar
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in non‐obese populations: Meta‐analytic assessment of its prevalence, genetic, metabolic, and histological profiles
Zi Yuan Zou, Vincent Wai‐Sun Wong, Jian Gao Fan
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2020; 21(7): 372. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Diagnosed Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Independently Predicts a Higher Risk of Developing Diabetes Mellitus in Nonoverweight Individuals
Liang Wang
Academic Radiology.2019; 26(7): 863. CrossRef - Blood Pressure and Development of Cardiovascular Disease in Koreans With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eun Sil Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Min-Kyung Lee, Ga Eun Nam, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Hypertension.2019; 73(2): 319. CrossRef - Understanding the association of polycystic ovary syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Nicolás Salva-Pastor, Norberto C. Chávez-Tapia, Misael Uribe, Natalia Nuño-Lámbarri
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2019; 194: 105445. CrossRef - Weight change and mortality and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with new-onset diabetes mellitus: a nationwide cohort study
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eun Sil Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Min-Kyung Lee, Ga Eun Nam, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Longitudinal analysis of risk of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in adulthood
Daniel J. Cuthbertson, Emily Brown, Juha Koskinen, Costan G. Magnussen, Nina Hutri‐Kähönen, Matthew Sabin, Päivi Tossavainen, Eero Jokinen, Tomi Laitinen, Jorma Viikari, Olli T. Raitakari, Markus Juonala
Liver International.2019; 39(6): 1147. CrossRef - Associations of Variability in Blood Pressure, Glucose and Cholesterol Concentrations, and Body Mass Index With Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the General Population
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Gunseog Kang, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
Circulation.2018; 138(23): 2627. CrossRef - The effects of metabolic status on non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease‐related outcomes, beyond the presence of obesity
Javier Ampuero, Rocío Aller, Rocío Gallego‐Durán, Jesus M. Banales, Javier Crespo, Carmelo García‐Monzón, María Jesús Pareja, Eduardo Vilar‐Gómez, Juan Caballería, Desamparados Escudero‐García, Judith Gomez‐Camarero, José Luis Calleja, Mercedes Latorre, A
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2018; 48(11-12): 1260. CrossRef - Dissecting the relationship between obesity and hyperinsulinemia: Role of insulin secretion and insulin clearance
Mee Kyoung Kim, Gerald M. Reaven, Sun H. Kim
Obesity.2017; 25(2): 378. CrossRef - The Effects of Exercise on Abdominal Fat and Liver Enzymes in Pediatric Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Katherine González-Ruiz, Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Jorge Enrique Correa-Bautista, Mark D. Peterson, Antonio García-Hermoso
Childhood Obesity.2017; 13(4): 272. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Emerging Burden in Cardiometabolic and Renal Diseases
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 430. CrossRef - Predictive Value of Triglyceride Glucose Index for the Risk of Incident Diabetes: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Da Young Lee, Eun Seo Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Fernando Guerrero-Romero
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(9): e0163465. CrossRef - Lean, but not healthy
Cherlyn Ding, Zhiling Chan, Faidon Magkos
Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care.2016; 19(6): 408. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Exendin-4 Inhibits the Expression of SEPP1 and Fetuin-A via Improvement of Palmitic Acid-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by AMPK
-
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):177-184. Published online June 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.177
-
-
4,510
View
-
45
Download
-
12
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Selenoprotein P (SEPP1) and fetuin-A, both circulating liver-derived glycoproteins, are novel biomarkers for insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. However, the effect of exendin-4 (Ex-4), a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, on the expression of hepatokines, SEPP1, and fetuin-A, is unknown. MethodsThe human hepatoma cell line HepG2 was treated with palmitic acid (PA; 0.4 mM) and tunicamycin (tuni; 2ug/ml) with or without exendin-4 (100 nM) for 24 hours. The change in expression of PA-induced SEPP1, fetuin-A, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers by exendin-4 treatment were evaluated using quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting. Transfection of cells with AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) small interfering RNA (siRNA) was performed to establish the effect of exendin-4-mediated AMPK in the regulation of SEPP1 and fetuin-A expression. ResultsExendin-4 reduced the expression of SEPP1, fetuin-A, and ER stress markers including PKR-like ER kinase, inositol-requiring kinase 1α, activating transcription factor 6, and C/EBP homologous protein in HepG2 cells. Exendin-4 also reduced the expression of SEPP1 and fetuin-A in cells treated with tunicamycin, an ER stress inducer. In cells treated with the AMPK activator 5-aminoidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), the expression of hepatic SEPP1 and fetuin-A were negatively related by AMPK, which is the target of exendin-4. In addition, exendin-4 treatment did not decrease SEPP1 and fetuin-A expression in cells transfected with AMPK siRNA. ConclusionThese data suggest that exendin-4 can attenuate the expression of hepatic SEPP1 and fetuin-A via improvement of PA-induced ER stress by AMPK.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Maternal Organic Selenium Supplementation Relieves Intestinal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Piglets by Enhancing the Expression of Glutathione Peroxidase 4 and Selenoprotein S
Dajiang Ding, Daolin Mou, Heng Zhu, Xuemei Jiang, Lianqiang Che, Zhengfeng Fang, Shengyu Xu, Yan Lin, Yong Zhuo, Jian Li, Chao Huang, Yuanfeng Zou, Lixia Li, De Wu, Bin Feng
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alliin, capsaicin, and gingerol attenuate endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic steatosis in HepG2 cells and C57BL/6N mice
Ye-Rang Yun, Ji-Eun Lee
Journal of Functional Foods.2022; 95: 105186. CrossRef - PNPLA3 I148M is involved in the variability in anti-NAFLD response to exenatide
Yunzhi Chen, Xuemei Yan, Xiao Xu, Shuhua Yuan, Fen Xu, Hua Liang
Endocrine.2020; 70(3): 517. CrossRef - Green tea extracts reduce leukocyte cell–Derived chemotaxin 2 and selenoprotein P levels in the livers of C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet
Shintaro Onishi, Hidefumi Kitazawa, Shinichi Meguro, Ichiro Tokimitsu
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry.2018; 82(9): 1568. CrossRef - Melatonin improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis through attenuation of alpha‐2‐HS‐glycoprotein
Jee‐In Heo, Dae Wui Yoon, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Nan Hee Kim
Journal of Pineal Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Palmitic acid induces ceramide accumulation, mitochondrial protein hyperacetylation, and mitochondrial dysfunction in porcine oocytes†
Nobuhiko Itami, Koumei Shirasuna, Takehito Kuwayama, Hisataka Iwata
Biology of Reproduction.2018; 98(5): 644. CrossRef - Astragaloside IV attenuates free fatty acid-induced ER stress and lipid accumulation in hepatocytes via AMPK activation
Bing Zhou, Dan-li Zhou, Xiao-hong Wei, Rong-yu Zhong, Jie Xu, Liao Sun
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2017; 38(7): 998. CrossRef - New Potential Targets of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Pancreatic β-Cells and Hepatocytes
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 1. CrossRef - Selenoprotein P neutralizes lipopolysaccharide and participates in hepatic cell endoplasmic reticulum stress response
Yongzhong Zhao, Shuvojit Banerjee, Ping Huang, Xinning Wang, Candece L. Gladson, Warren D. Heston, Charles B. Foster
FEBS Letters.2016; 590(24): 4519. CrossRef - Novel phenotypes of prediabetes?
Hans-Ulrich Häring
Diabetologia.2016; 59(9): 1806. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Comparison of Serum Adipocytokine Levels according to Metabolic Health and Obesity Status
-
Tae Hoon Lee, Won Seon Jeon, Ki Joong Han, Shin Yeoung Lee, Nam Hee Kim, Hyun Beom Chae, Choel Min Jang, Kyung Mo Yoo, Hae Jung Park, Min Kyung Lee, Se Eun Park, Hyung Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):185-194. Published online June 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.185
-
-
4,635
View
-
34
Download
-
16
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Metabolic health is an emerging concept that is highly correlated with various metabolic complications, and adipocytokines have been causally linked to a wide range of metabolic diseases. Thus, this study compared serum adipocytokine levels according to metabolic health and obesity status. MethodsFour hundred and fifty-six nondiabetic subjects (mean age, 40.5 years) were categorized into four groups according to metabolic health and obesity status: metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO), metabolically healthy obese (MHO), metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUHNO), and metabolically unhealthy obese (MUHO). Being metabolically healthy was defined as the presence of fewer than two of the following five metabolic abnormalities: high blood pressure, high fasting blood glucose, high triglyceride, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and being in the highest decile of the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance index. Obesity status was assessed using body mass index (BMI), with obesity defined as a BMI higher than 25 kg/m2. Levels of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (A-FABP) were also evaluated. ResultsOf the 456 subjects, 247 (54.2%) were in the MHNO group, 66 (14.5%) were in the MHO group, 66 (14.5%) were in the MUHNO group, and 77 (16.9%) were in the MUHO group. There were no significant differences in IL-6 or MCP-1 levels among the groups, but levels of TNF-α and A-FABP were significantly higher in the MUHNO group compared to the MHNO group. ConclusionHigh TNF-α and A-FABP levels are significantly associated with metabolically unhealthiness in nonobese Korean individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Differences in the levels of inflammatory markers between metabolically healthy obese and other obesity phenotypes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhouli Su, Ljupcho Efremov, Rafael Mikolajczyk
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(2): 251. CrossRef - Relationship between the thrombospondin-1/Toll-like receptor 4 (TSP1/TLR4) pathway and vitamin D levels in obese and normal weight subjects with different metabolic phenotypes
Eman Y. Khairy, Azza Saad
The Journal of Physiological Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pattern of Adiponectin, Osteocalcin, Irisin, FGF-21, and MCP-1 According to the Body Size Phenotype: Could They Be Markers of Metabolic Health in Mexican-Mestizo Middle-Aged Women?
Lourdes Balcázar-Hernandez, Lourdes Basurto, Leticia Manuel-Apolinar, Sara Vega-García, Norma Basurto-Acevedo, Carlos Martínez-Murillo, Rosalinda Sánchez-Arenas
Metabolites.2021; 11(11): 771. CrossRef - Exploring Therapeutic Targets to Reverse or Prevent the Transition from Metabolically Healthy to Unhealthy Obesity
Tenzin D. Dagpo, Christopher J. Nolan, Viviane Delghingaro-Augusto
Cells.2020; 9(7): 1596. CrossRef - Poor Vitamin D Status in Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients and Its Correlation with Leptin and TNF-α
Qiuzhen WANG, Aiguo MA, Tianlin GAO, Yufeng LIU, Lisheng REN, Lei HAN, Boyang WEI, Qian LIU, Chunjiang DONG, Yuze MU, Duo LI, Frans J KOK, Evert G SCHOUTEN
Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology.2019; 65(5): 390. CrossRef - Metabolic Health—The Role of Adipo-Myokines
Christine Graf, Nina Ferrari
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(24): 6159. CrossRef - Does the Metabolically Healthy Obese Phenotype Protect Adults with Class III Obesity from Biochemical Alterations Related to Bone Metabolism?
Ligiane Marques Loureiro, Suzane Lessa, Rodrigo Mendes, Sílvia Pereira, Carlos José Saboya, Andrea Ramalho
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2125. CrossRef - Being Metabolically Healthy, the Most Responsible Factor for Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Association between Serum Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Concentration and Obesity-related Factors in Health Screen Examinees
Ji Yeon Lee, Byoung Kuk Jang, Min Kyung Song, Hye Soon Kim, Mi-Kyung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(3): 188. CrossRef - Kofaktoren und Komorbiditäten bei Necrobiosis lipoidica – Analyse der deutschen DRG‐Daten von 2012
Finja Jockenhöfer, Knut Kröger, Joachim Klode, Regina Renner, Cornelia Erfurt‐Berge, Joachim Dissemond
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2016; 14(3): 277. CrossRef - The relationship between serum fatty-acid binding protein 4 level and lung function in Korean subjects with normal ventilatory function
Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Seong Yong Lim, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Cofactors and comorbidities of necrobiosis lipoidica: analysis of the German DRG data from 2012
Finja Jockenhöfer, Knut Kröger, Joachim Klode, Regina Renner, Cornelia Erfurt‐Berge, Joachim Dissemond
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2016; 14(3): 277. CrossRef - Response: Comparison of Serum Adipocytokine Levels according to Metabolic Health and Obesity Status (Endocrinol Metab2015;30:185-94, Tae Hoon Lee et al.)
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 416. CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of Serum Adipocytokine Levels according to Metabolic Health and Obesity Status (Endocrinol Metab2015;30:185-94, Tae Hoon Lee et al.)
Mikyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 414. CrossRef - Adipokine Profiles and Metabolic Health
Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(2): 175. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- 2014 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Overweight and Obesity in Korea
-
Mee Kyoung Kim, Won-Young Lee, Jae-Heon Kang, Jee-Hyun Kang, Bom Taeck Kim, Seon Mee Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Sang-Hoon Suh, Hye Jung Shin, Kyu Rae Lee, Ki Young Lee, Sang Yeoup Lee, Seon Yeong Lee, Seong-Kyu Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Sochung Chung, In Kyung Jeong, Kyung Yul Hur, Sung Soo Kim, Jeong-taek Woo
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):405-409. Published online December 29, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.405
-
-
8,893
View
-
80
Download
-
228
Web of Science
-
247
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
The dramatic increase in the prevalence of obesity and its accompanying comorbidities are major health concerns in Korea. Obesity is defined as a body mass index ≥25 kg/m2 in Korea. Current estimates are that 32.8% of adults are obese: 36.1% of men and 29.7% of women. The prevalence of being overweight and obese in national surveys is increasing steadily. Early detection and the proper management of obesity are urgently needed. Weight loss of 5% to 10% is the standard goal. In obese patients, control of cardiovascular risk factors deserves the same emphasis as weight-loss therapy. Since obesity is multifactorial, proper care of obesity requires a coordinated multidisciplinary treatment team, as a single intervention is unlikely to modify the incidence or natural history of obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Increased Risk of Diabetes Development in Subjects with the Hypertriglyceridemic Waist Phenotype: A 4-Year Longitudinal Study
-
Ki Joong Han, Shin Yeoung Lee, Nam Hee Kim, Hyun Beom Chae, Tae Hoon Lee, Choel Min Jang, Kyung Mo Yoo, Hae Jung Park, Min Kyung Lee, Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):514-521. Published online December 29, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.514
-
-
4,536
View
-
30
Download
-
21
Web of Science
-
21
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
The hypertriglyceridemic waist (HTGW) phenotype is a simple and inexpensive screening parameter to identify people at increased risk of cardiovascular disease. We evaluated whether the HTGW phenotype predicts diabetes in urban Korean adults. MethodsA total of 2,900 nondiabetic subjects (mean age 44.3 years), comprising 2,078 males (71.7%) and 822 females (28.3%) who underwent annual medical check-ups at our center between January 2005 and December 2009, were recruited. The subjects were divided into four groups according to baseline serum triglyceride (TG) level and waist circumference (WC): normal WC-normal TG (NWNT) level, normal WC-high TG level, enlarged WC-normal TG level, and enlarged WC-high TG (EWHT) level. High serum TG level was defined as ≥150 mg/dL and enlarged WC was defined as ≥90 cm for men and ≥85 cm for women. New cases of diabetes were determined according to questionnaires filled in by participants and the diagnostic criteria of the American Diabetes Association. Cox proportional hazards model analysis was used to assess the association of HTGW phenotype with the incidence of diabetes. ResultsA total of 101 (3.5%) new diabetes cases were diagnosed during the study period. The EWHT group had a higher incidence of diabetes (8.3%) compared with the NWNT group (2.2%). The adjusted hazard ratio for diabetes for subjects with the EWHT phenotype at baseline was 4.113 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.397 to 7.059) after adjustment for age, and 2.429 (95% CI, 1.370 to 4.307) after adjustment for age, sex, total cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, and alcohol drinking history. It was attenuated by inclusion of baseline fasting glucose level in the model. ConclusionSubjects with the HTGW phenotype showed the highest risk of incident diabetes. This tool could be useful for identifying individuals at high risk of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Triglyceridemic Waist Phenotypes as Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Fiorella E. Zuzunaga-Montoya, Víctor Juan Vera-Ponce
International Journal of Statistics in Medical Research.2024; 13: 19. CrossRef - Association between hypertriglyceridemic-waist phenotype and circadian syndrome risk: a longitudinal cohort study
Li-Kun Hu, Yu-Hong Liu, Kun Yang, Ning Chen, Lin-Lin Ma, Yu-Xiang Yan
Hormones.2023; 22(3): 457. CrossRef - Caracterización del fenotipo de cintura hipertrigliceridémica en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 en España: un estudio epidemiológico
I. Miñambres, J. Sánchez-Hernández, G. Cuixart, A. Sánchez-Pinto, J. Sarroca, A. Pérez
Revista Clínica Española.2021; 221(10): 576. CrossRef - Association of “hypertriglyceridemic waist” with increased 5-year risk of subclinical atherosclerosis in a multi-ethnic population: a prospective cohort study
Peyman Namdarimoghaddam, Adeleke Fowokan, Karin H. Humphries, G. B. John Mancini, Scott Lear
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization of the hypertriglyceridemic waist phenotype in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Spain: an epidemiological study
I. Miñambres, J. Sánchez-Hernandez, G. Cuixart, A. Sánchez-Pinto, J. Sarroca, A. Pérez
Revista Clínica Española (English Edition).2021; 221(10): 576. CrossRef - Association between Hypertriglyceridemic-Waist Phenotype and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged and Older Chinese Population: A Longitudinal Cohort Study
Dezhong Chen, Ziyun Liang, Huimin Sun, Ciyong Lu, Weiqing Chen, Harry H. X. Wang, Vivian Yawei Guo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9618. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome, and Particularly the Hypertriglyceridemic-Waist Phenotype, Increases Breast Cancer Risk, and Adiponectin Is a Potential Mechanism: A Case–Control Study in Chinese Women
Yujuan Xiang, Wenzhong Zhou, Xuening Duan, Zhimin Fan, Shu Wang, Shuchen Liu, Liyuan Liu, Fei Wang, Lixiang Yu, Fei Zhou, Shuya Huang, Liang Li, Qiang Zhang, Qinye Fu, Zhongbing Ma, Dezong Gao, Shude Cui, Cuizhi Geng, Xuchen Cao, Zhenlin Yang, Xiang Wang,
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemic Waist Phenotype and Lipid Accumulation Product: Two Comprehensive Obese Indicators of Waist Circumference and Triglyceride to Predict Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Population
Minrui Xu, Mingtao Huang, Deren Qiang, Jianxin Gu, Yong Li, Yingzi Pan, Xingjuan Yao, Wenchao Xu, Yuan Tao, Yihong Zhou, Hongxia Ma, Ulrike Rothe
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and relationship of hypertriglyceridaemic–waist phenotype and type 2 diabetes mellitus among a rural adult Chinese population
Yong-Cheng Ren, Yu Liu, Xi-Zhuo Sun, Bing-Yuan Wang, Yi Liu, Hu Ni, Yang Zhao, Dechen Liu, Xuejiao Liu, Dongdong Zhang, Feiyan Liu, Cheng Cheng, Leilei Liu, Xu Chen, Qionggui Zhou, Ming Zhang, Dongsheng Hu
Public Health Nutrition.2019; 22(8): 1361. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemic waist phenotype and abnormal glucose metabolism: a system review and meta-analysis
Chun-Ming Ma, Xiao-Li Liu, Na Lu, Rui Wang, Qiang Lu, Fu-Zai Yin
Endocrine.2019; 64(3): 469. CrossRef - Superior Role of Waist Circumference to Body-Mass Index in the Prediction of Cardiometabolic Risk in Dyslipidemic Patients
Ľ. Cibičková, K. Langová, H. Vaverková, J. Lukeš, N. Cibiček
Physiological Research.2019; : 931. CrossRef - Being Metabolically Healthy, the Most Responsible Factor for Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Letter: Utility of the Visceral Adiposity Index and Hypertriglyceridemic Waist Phenotype for Predicting Incident Hypertension (Endocrinol Metab 2017;32:221-9, Mohsen Janghorbani et al.)
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(3): 396. CrossRef - The Relationship between Hypertriglyceridemic Waist Phenotype and Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Chun-Ming Ma, Rui Wang, Xiao-Li Liu, Na Lu, Qiang Lu, Fu-Zai Yin
Cardiorenal Medicine.2017; 7(4): 295. CrossRef - The Association of Hypertriglyceridemic Waist Phenotype with Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Sex Difference: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Urban Chinese Elderly Population
Jing Zeng, Miao Liu, Lei Wu, Jianhua Wang, Shanshan Yang, Yiyan Wang, Yao Yao, Bin Jiang, Yao He
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2016; 13(12): 1233. CrossRef - Prevalence of hypertriglyceridemic waist and association with risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta‐analysis
Yongcheng Ren, Xinping Luo, Chongjian Wang, Lei Yin, Chao Pang, Tianping Feng, Bingyuan Wang, Lu Zhang, Linlin Li, Xiangyu Yang, Hongyan Zhang, Jingzhi Zhao, Dongsheng Hu
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2016; 32(4): 405. CrossRef - Utility of hypertriglyceridemic waist phenotype for predicting incident type 2 diabetes: The Isfahan Diabetes Prevention Study
Mohsen Janghorbani, Masoud Amini
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2016; 7(6): 860. CrossRef - βig-h3 Represses T-Cell Activation in Type 1 Diabetes
Maeva Patry, Romain Teinturier, Delphine Goehrig, Cornelia Zetu, Doriane Ripoche, In-San Kim, Philippe Bertolino, Ana Hennino
Diabetes.2015; 64(12): 4212. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemic Waist – a Simple Clinical Tool to Detect Cardiometabolic Risk: Comparison With Harmonized Definition of Metabolic Syndrome
H. VAVERKOVÁ, D. KARÁSEK, D. NOVOTNÝ, M. HALENKA, J. ORSÁG, L. SLAVÍK
Physiological Research.2015; : S385. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Changes in Metabolic Health Status Over Time and Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Seung-Hwan Lee, Hae Kyung Yang, Hee-Sung Ha, Jin-Hee Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Hyeon-Woo Yim, Moo-Il Kang, Won-Chul Lee, Ho-Young Son, Kun-Ho Yoon
Medicine.2015; 94(40): e1705. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Attenuates Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Lipolysis via Protection of Perilipin in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
-
Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):553-560. Published online December 29, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.553
-
-
3,403
View
-
26
Download
-
12
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) are known to stimulate and repress lipolysis in adipocytes, respectively; however, the mechanisms regulating these processes have not been completely elucidated. MethodsThe key factors and mechanism of action of TNF-α and AMPK in lipolysis were investigated by evaluating perilipin expression and activity of protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)/eukaryotic initiation factor 2 α (eIF2α) by Western blot and an immunofluorescence assay in 24-hour TNF-α-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes with artificial manipulation of AMPK activation. ResultsEnhancement of AMPK activity by the addition of activator minoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) suppressed TNF-α-induced lipolysis, whereas the addition of compound C, an inhibitor of AMPK phosphorylation, enhanced lipolysis. Perilipin, a lipid droplet-associated protein, was decreased by TNF-α and recovered following treatment with AICAR, showing a correlation with the antilipolytic effect of AICAR. Significant activation of PERK/eIF2α, a component of the unfolded protein response signaling pathway, was observed in TNF-α or vesicle-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The antilipolytic effect and recovery of perilipin expression by AICAR in TNF-α-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were significantly diminished by treatment with 2-aminopurine, a specific inhibitor of eIF2α. ConclusionThese data indicated that AICAR-induced AMPK activation attenuates TNF-α-induced lipolysis via preservation of perilipin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In addition, PERK/eIF2α activity is a novel mechanism of the anti-lipolytic effect of AICAR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Dysregulation of Lipid Droplet Protein Expression in Adipose Tissues and Association with Metabolic Risk Factors in Adult Females with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Chan Yoon Park, Donguk Kim, Min Kyeong Seo, Jimin Kim, Han Choe, Jong-Hyeok Kim, Joon Pio Hong, Yeon Ji Lee, Yoonseok Heo, Hwa Jung Kim, Hye Soon Park, Yeon Jin Jang
The Journal of Nutrition.2023; 153(3): 691. CrossRef - Tschimganidine reduces lipid accumulation through AMPK activation and alleviates high-fat diet-induced metabolic diseases
Min-Seon Hwang, Jung-Hwan Baek, Jun-Kyu Song, In Hye Lee, Kyung-Hee Chun
BMB Reports.2023; 56(4): 246. CrossRef - Acetate stimulates lipogenesis via AMPKα signaling in rabbit adipose-derived stem cells
Lei Liu, Chunyan Fu, Yongxu Liu, Fuchang Li
General and Comparative Endocrinology.2021; 303: 113715. CrossRef - Docosahexaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids and eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by activating sirtuin 1 pathways
Yu-Hong Yang, Yi-Ming Hao, Xiao-Fang Liu, Xiang Gao, Bao-Zhen Wang, Koretaro Takahashi, Lei Du
Food & Function.2021; 12(11): 4783. CrossRef - Role of the AMPK/ACC Signaling Pathway in TRPP2-Mediated Head and Neck Cancer Cell Proliferation
Kun Li, Lei Chen, Zhangying Lin, Junwei Zhu, Yang Fang, Juan Du, Bing Shen, Kaile Wu, Yehai Liu, Gianmarco Saponaro
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - GLUT12 and adipose tissue: Expression, regulation and its relation with obesity in mice
Eva Gil‐Iturbe, José Miguel Arbones‐Mainar, María J. Moreno‐Aliaga, María Pilar Lostao
Acta Physiologica.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Bilobalide Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes via the AMPK Signaling Pathway
Su Bu, Chun Ying Yuan, Quan Xue, Ying Chen, Fuliang Cao
Molecules.2019; 24(19): 3503. CrossRef - Sulforaphane induces adipocyte browning and promotes glucose and lipid utilization
Hui Q. Zhang, Shi Y. Chen, An S. Wang, An J. Yao, Jian F. Fu, Jin S. Zhao, Fen Chen, Zu Q. Zou, Xiao H. Zhang, Yu J. Shan, Yong P. Bao
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2016; 60(10): 2185. CrossRef - Fyn phosphorylates AMPK to inhibit AMPK activity and AMP-dependent activation of autophagy
Eijiro Yamada, Shuichi Okada, Claire C. Bastie, Manu Vatish, Yasuyo Nakajima, Ryo Shibusawa, Atsushi Ozawa, Jeffrey E. Pessin, Masanobu Yamada
Oncotarget.2016; 7(46): 74612. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Age Is the Strongest Effector for the Relationship between Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate and Coronary Artery Calcification in Apparently Healthy Korean Adults
-
Hyun Beom Chae, Shin Yeoung Lee, Nam Hee Kim, Ki Joong Han, Tae Hoon Lee, Choel Min Jang, Kyung Mo Yoo, Hae Jung Park, Min Kyung Lee, Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Heui-Soo Moon, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):312-319. Published online September 25, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.312
-
-
3,727
View
-
33
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is considered one of the most common risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Coronary artery calcification (CAC) is a potential mechanism that explains the association between renal function and cardiovascular mortality. We aimed to evaluate the association between renal function and CAC in apparently healthy Korean subjects. MethodsA total of 23,617 participants in a health-screening program at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital were included in the study. Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was assessed using the Cockcroft-Gault equation. Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) was measured via multidetector computed tomography. Subjects were divided into three groups according to the CKD Staging system with eGFR grade: stage 1, eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; stage 2, eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2; and stage 3, eGFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m2. ResultsThe mean age of the participants was 41.4 years and the mean eGFR was 103.6±21.7 mL/min/1.73 m2. Hypertension and diabetes were noted in 43.7% and 5.5% of the participants, respectively. eGFR showed a weakly negative but significant association with CACS in bivariate correlation analysis (r=-0.076, P<0.01). Mean CACS significantly increased from CKD stage 1 to 3. The proportion of subjects who had CAC significantly increased from CKD stage 1 to 3. Although the odds ratio for CAC significantly increased from stage 1 to 3 after adjustment for confounding factors, this significance was reversed when age was included in the model. ConclusionIn early CKD, renal function negatively correlated with the degree of CAC in Korean subjects. Age was the strongest effector for this association.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Coronary artery calcium and risk of chronic kidney disease in young and middle-aged adults
Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Yoosoo Chang, Young Youl Hyun, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hocheol Shin, Sarah H Wild, Christopher D Byrne, Seungho Ryu
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023; 38(6): 1439. CrossRef - New Model for Predicting the Presence of Coronary Artery Calcification
Samel Park, Min Hong, HwaMin Lee, Nam-jun Cho, Eun-Young Lee, Won-Young Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyo-Wook Gil
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(3): 457. CrossRef - Long-term effects of various types of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on changes in glomerular filtration rate in Korea
Seo Yeon Baik, Hyunah Kim, So Jung Yang, Tong Min Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Frontiers of Medicine.2019; 13(6): 713. CrossRef - Chronic kidney disease and coronary artery calcification in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA‐Brasil)
Cheng Suh‐Chiou, Rosa M. Moysés, Marcio S. Bittencourt, Isabela M. Bensenor, Paulo A. Lotufo
Clinical Cardiology.2017; 40(12): 1309. CrossRef - Eligibility for Statin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Reduced Renal Function: An Observational Study
Byung Sub Moon, Jongho Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hyang Kim, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 402. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Serum Adipocyte-Specific Fatty Acid Binding Protein with Fatty Liver Index as a Predictive Indicator of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
-
Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(4):283-287. Published online December 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.4.283
-
-
3,419
View
-
33
Download
-
15
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Adipocyte-specific fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP) is a cytoplasmic protein expressed in macrophages and adipocytes and it plays a role in insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Recently, the fatty liver index (FLI) was introduced as an indicator of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study, we aimed to investigate the relationship between baseline serum A-FABP levels and FLI after 4 years in apparently healthy subjects. MethodsA total of 238 subjects without a past history of alcoholism or hepatitis were recruited from a medical check-up program. The NAFLD state was evaluated 4 years later in the same subjects using FLI. Fatty liver disease was diagnosed as diffusely increased echogenicity of the hepatic parenchyma compared to the kidneys, vascular blurring, and deep-echo attenuation. NAFLD was defined as subjects with fatty liver and no history of alcohol consumption (>20 g/day). ResultsBaseline serum A-FABP levels were significantly associated with FLI after adjustment for age and sex (P<0.001). The subjects with higher A-FABP levels had a higher mean FLI (P for trend=0.006). After adjusting for age and sex, serum A-FABP levels at baseline were shown to be significantly associated with FLI as a marker of development of NAFLD after 4 years (odds ratio, 2.68; 95% confidence interval, 1.24 to 5.80 for highest tertile vs. lowest tertile; P=0.012). ConclusionThis study demonstrated that higher baseline serum A-FABP levels were associated with FLI as a predictive indicator of NAFLD after 4 years of follow-up in healthy Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - FABP4 Expression in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Is Independently Associated with Circulating Triglycerides in Obesity
Óscar Osorio-Conles, Ainitze Ibarzabal, José María Balibrea, Josep Vidal, Emilio Ortega, Ana de Hollanda
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(3): 1013. CrossRef - Unveiling the Role of the Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in the Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Juan Moreno-Vedia, Josefa Girona, Daiana Ibarretxe, Lluís Masana, Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 197. CrossRef - Circulating level of fatty acid‐binding protein 4 is an independent predictor of metabolic dysfunction‐associated fatty liver disease in middle‐aged and elderly individuals
Marenao Tanaka, Satoko Takahashi, Yukimura Higashiura, Akiko Sakai, Masayuki Koyama, Shigeyuki Saitoh, Kazuaki Shimamoto, Hirofumi Ohnishi, Masato Furuhashi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(5): 878. CrossRef - New Insights into Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Coronary Artery Disease: The Liver-Heart Axis
Georgiana-Diana Cazac, Cristina-Mihaela Lăcătușu, Cătălina Mihai, Elena-Daniela Grigorescu, Alina Onofriescu, Bogdan-Mircea Mihai
Life.2022; 12(8): 1189. CrossRef - Association between the liver fat score (LFS) and cardiovascular diseases in the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999–2016
Chun-On Lee, Hang-Long Li, Man-Fung Tsoi, Ching-Lung Cheung, Bernard Man Yung Cheung
Annals of Medicine.2021; 53(1): 1067. CrossRef - Relationship Between Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 and Liver Fat in Individuals at Increased Cardiometabolic Risk
Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo, Juan Moreno-Vedia, Josefa Girona, Daiana Ibarretxe, Neus Martínez-Micaelo, Jordi Merino, Nuria Plana, Lluis Masana
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: An Epidemiological Perspective
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 226. CrossRef - Serum adipocyte fatty acid‐binding protein levels: An indicator of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese individuals
Yiting Xu, Xiaojing Ma, Xiaoping Pan, Xingxing He, Yufei Wang, Yuqian Bao
Liver International.2019; 39(3): 568. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - The relationship between serum fatty-acid binding protein 4 level and lung function in Korean subjects with normal ventilatory function
Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Seong Yong Lim, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a diagnostic marker for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Erdem Akbal, Erdem Koçak, Ömer Akyürek, Seyfettin Köklü, Hikmetullah Batgi, Mehmet Şenes
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2016; 128(1-2): 48. CrossRef - High‐methionine diets accelerate atherosclerosis by HHcy‐mediated FABP4 gene demethylation pathway via DNMT1 in ApoE−/− mice
An-Ning Yang, Hui-Ping Zhang, Yue Sun, Xiao-Ling Yang, Nan Wang, Guangrong Zhu, Hui Zhang, Hua Xu, Sheng-Chao Ma, Yue Zhang, Gui-Zhong Li, Yue-Xia Jia, Jun Cao, Yi-Deng Jiang
FEBS Letters.2015; 589(24PartB): 3998. CrossRef - Metabolic Health Is More Important than Obesity in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
Min-Kyung Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Jeong In Lee, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 522. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Noninvasive Markers for the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Sang Yong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(4): 280. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- The Relationship of Body Composition and Coronary Artery Calcification in Apparently Healthy Korean Adults
-
Jung-Hee Yu, Seo Hyoung Yim, Su Hyeon Yu, Ji Yong Lee, Jong Dae Kim, Mi Hae Seo, Won Seon Jeon, Se-Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(1):33-40. Published online March 25, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.1.33
-
-
3,948
View
-
29
Download
-
24
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader
- Background
We investigated the association of coronary artery calcium score (CACS) with body composition and insulin resistance in apparently healthy Korean adults. MethodsNine hundred forty-five participants (mean age, 48.9 years; 628 men) in a medical check-up program were selected for analysis. Body composition was assessed by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). Insulin resistance was evaluated using the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). The CACS was assessed by multidetector computed tomography. ResultsOne hundred forty-six subjects (15.4%) showed coronary artery calcification and 148 subjects (15.7%) had metabolic syndrome. CACS showed a significant positive correlation with age, fasting glucose level, waist circumference (WC), blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, HOMA-IR, and waist-hip ratio (WHR) assessed by BIA. CACS had a negative correlation with high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Subjects with high CACS showed significantly higher mean WHRs and lower mean values for lean body mass compared with subjects without coronary artery calcification. In logistic regression analyses with coronary artery calcification as the dependent variable, the highest quartile of WHR showed a 3.125-fold increased odds ratio for coronary artery calcification compared with the lowest quartile after adjustment for confounding variables. When receiver operating characteristics analyses were performed with coronary artery calcification as the result variable, WHR showed the largest area under the curve (AUC) value among other variables except for age and WC in women (AUC=0.696 for WHR, 0.790 for age, and 0.719 for WC in women). ConclusionIn our study population of apparently healthy Korean adults, WHR was the most significant predictor for coronary artery calcification among other confounding factors, suggesting that it may have implication as a marker for early atherosclerosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Body weight at age 20 and in midlife is more important than weight gain for coronary atherosclerosis: Results from SCAPIS
Göran Bergström, Annika Rosengren, Elin Bacsovics Brolin, John Brandberg, Kerstin Cederlund, Gunnar Engström, Jan E. Engvall, Maria J. Eriksson, Isabel Gonçalves, Emil Hagström, Stefan K. James, Tomas Jernberg, Mikael Lilja, Martin Magnusson, Anders Perss
Atherosclerosis.2023; 373: 46. CrossRef - Association Between Measures of Body Composition and Coronary Calcium: Findings From the Multi‐Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Tamara Horwich, Preethi Srikanthan, Anisha Gaitonde, Karol Watson, Matthew Allison, Richard Kronmal
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pericardial fat, thoracic peri-aortic adipose tissue, and systemic inflammatory marker in nonalcoholic fatty liver and abdominal obesity phenotype
Chun-Ho Yun, Jing-Rong Jhuang, Meng-Ting Tsou
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender-Based Association of Coronary Artery Calcification and Framingham Risk Score With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Abdominal Obesity in Taiwanese Adults, a Cross-Sectional Study
Meng-Ting Tsou, Jau-Yuan Chen
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - New Model for Predicting the Presence of Coronary Artery Calcification
Samel Park, Min Hong, HwaMin Lee, Nam-jun Cho, Eun-Young Lee, Won-Young Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyo-Wook Gil
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(3): 457. CrossRef - Association between waist-hip ratio and coronary artery calcification in postmenopausal women
Youngmi Eun, Su Nam Lee, Jin Jung, Min Sik Kim, Keon-Woong Moon, Ki-Dong Yoo
Menopause.2020; 27(9): 1010. CrossRef - Being Metabolically Healthy, the Most Responsible Factor for Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Moderate Beer Intake and Cardiovascular Health in Overweight Individuals
Teresa Padro, Natàlia Muñoz-García, Gemma Vilahur, Patricia Chagas, Alba Deyà, Rosa Antonijoan, Lina Badimon
Nutrients.2018; 10(9): 1237. CrossRef - Effects of Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol on Coronary Artery Calcification Progression According to High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels
Da Young Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Se Eun Park, Cheol-young Park, Ki-won Oh, Sung-woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-young Lee
Archives of Medical Research.2017; 48(3): 284. CrossRef - Decreased muscle mass in Korean subjects with intracranial arterial stenosis: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Ho-Jung Jung, Hwanseok Jung, Taeyoung Lee, Jongho Kim, Jongsin Park, Hacsoo Kim, Junghwan Cho, Won-Young Lee, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyung-Geun Oh
Atherosclerosis.2017; 256: 89. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of statin prescription patterns and outcomes according to clinical department
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, H. Lee, B. Park, S. Park, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, H. Song, J. H. Kim, K.-H. Yoon, I. Y. Choi
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(1): 70. CrossRef - Increased risk for development of coronary artery calcification in insulin-resistant subjects who developed diabetes: 4-year longitudinal study
Eun-Jung Rhee, Ji Hyun Kim, Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park
Atherosclerosis.2016; 245: 132. CrossRef - Waist Circumference as a Marker of Obesity Is More Predictive of Coronary Artery Calcification than Body Mass Index in Apparently Healthy Korean Adults: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Jongsin Park, Eun Seo Lee, Da Young Lee, Jihyun Kim, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(4): 559. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Progression of Coronary Artery Calcification in Male Subjects with High Baseline Waist-to-Height Ratio: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Hyung-Geun Oh, Shriram Nallamshetty, Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(1): 54. CrossRef - Characteristics of Body Composition and Muscle Strength of North Korean Refugees during South Korean Stay
Sun Wook Cho, So Hee Lee, Eun Sil Koh, Si Eun Kim, Seok Joong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 551. CrossRef - Higher association of coronary artery calcification with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than with abdominal obesity in middle-aged Korean men: the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Min-Kyung Lee, Hye-Jeong Park, Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Risk for Intracranial Arterial Stenosis in Subjects With Coronary Artery Calcification
Hyung-Geun Oh, Pil-Wook Chung, Eun-Jung Rhee
Stroke.2015; 46(1): 151. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome criteria as predictors of subclinical atherosclerosis based on the coronary calcium score
Mi Hae Seo, Eun-Jung Rhee, Se Eun Park, Cheol Young Park, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2015; 30(1): 73. CrossRef - Statin eligibility and cardiovascular risk burden assessed by coronary artery calcium score: Comparing the two guidelines in a large Korean cohort
Eun-Jung Rhee, Se Eun Park, Hyung Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Ron Blankstein, Jorge Plutzky, Won-Young Lee
Atherosclerosis.2015; 240(1): 242. CrossRef - Relationship of Glycated Hemoglobin A1c, Coronary Artery Calcification and Insulin Resistance in Males Without Diabetes
Chan-Hee Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kyu-Jin Kim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Se Eun Park, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Cheol-Young Park, Ji-Oh Mok, Ki-Won Oh, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Woo Park, Sung-Koo Kang, Won-Young Lee
Archives of Medical Research.2015; 46(1): 71. CrossRef - Metabolic Health Is a More Important Determinant for Diabetes Development than Simple Obesity: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Eun-Jung Rhee, Min Kyung Lee, Jong Dae Kim, Won Seon Jeon, Ji Cheol Bae, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee, Reury F. P. Bacurau
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(5): e98369. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Letter: The Relationship of Body Composition and Coronary Artery Calcification in Apparently Healthy Korean Adults (Endocrinol Metab 2013;28:33-40, Jung-Hee Yu et al.)
Han Seok Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(2): 153. CrossRef - Metabolic Health Is More Closely Associated with Coronary Artery Calcification than Obesity
Eun-Jung Rhee, Mi Hae Seo, Jong Dae Kim, Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee, Rozemarijn Vliegenthart
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(9): e74564. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Tumor Necrosis Factor-α as a Predictor for the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Follow-Up Study
-
Yun Yong Seo, Yong Kyun Cho, Ji-Cheol Bae, Mi Hae Seo, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(1):41-45. Published online March 25, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.1.41
-
-
4,537
View
-
34
Download
-
60
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α is associated with insulin resistance and systemic inflammatory responses. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between TNF-α and the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a longitudinal study. MethodsThree hundred and sixty-three apparently healthy subjects (mean age, 40.5±6.1 years; male, 57.6%) without NAFLD were enrolled in 2003. Anthropometric and laboratory measurements were performed. The participants were grouped into tertiles according to their serum TNF-α levels from samples taken in 2003. At a 4-year follow-up, we compared the odds ratios (ORs) of the development of NAFLD according to the tertiles of TNF-α levels measured in 2003. ResultsAt the 4-year follow-up, the cumulative incidence of NAFLD was 29.2% (106/363). The group that developed NAFLD had higher levels of TNF-α than those in the group without NAFLD (3.65±1.79 pg/mL vs. 3.15±1.78 pg/mL; P=0.016). When the 2003 serum TNF-α levels were categorized into tertiles: incidence of NAFLD observed in 2007 was significantly higher with increasing tertiles (22.6%, 35.8%, and 41.5%, respectively; P<0.05). The risk of developing NAFLD was significantly greater in the highest tertile of TNF-α than in the lowest tertile after adjusting for age, smoking, and BMI (OR, 2.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.12 to 4.01; P<0.05). ConclusionHigher serum TNF-α levels in subjects without NAFLD were associated with the development of NAFLD. The results of study might suggest a pathologic role of inflammation in NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 
- Impact of Antidiabetic Drugs on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
-
Han Na Jang, Sun Joon Moon, Jin Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
-
Received October 16, 2023 Accepted January 3, 2024 Published online January 29, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1857
[Epub ahead of print]
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Inconsistent results have been reported regarding the association between the use of antidiabetic drugs and the clinical outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to investigate the effect of antidiabetic drugs on COVID-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes using data from the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) in South Korea.
Methods
We analyzed the NHIS data of patients aged ≥20 years who tested positive for COVID-19 and were taking antidiabetic drugs between December 2019 and June 2020. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 based on the use of antidiabetic drugs.
Results
A total of 556 patients taking antidiabetic drugs tested positive for COVID-19, including 271 male (48.7%), most of whom were in their sixties. Of all patients, 433 (77.9%) were hospitalized, 119 (21.4%) received oxygen treatment, 87 (15.6%) were admitted to the intensive care unit, 31 (5.6%) required mechanical ventilation, and 61 (11.0%) died. Metformin was significantly associated with the lower risks of mechanical ventilation (odds ratio [OR], 0.281; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.109 to 0.720; P=0.008), and death (OR, 0.395; 95% CI, 0.182 to 0.854; P=0.018). Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) were significantly associated with the lower risks of oxygen treatment (OR, 0.565; 95% CI, 0.356 to 0.895; P=0.015) and death (OR, 0.454; 95% CI, 0.217 to 0.949; P=0.036). Sulfonylurea was significantly associated with the higher risk of mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.579; 95% CI, 1.004 to 6.626; P=0.049).
Conclusion
In patients with diabetes and COVID-19, metformin exhibited reduced risks of mechanical ventilation and death, DPP- 4i was linked with lower risks of oxygen treatment and death, while sulfonylurea was related to the increased risk of mechanical ventilation.
|